Overview
Skin cancer is the rapid growth of abnormal skin cells. Most common cause of skin cancer is over exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light radiation of the sun, but not in every case.
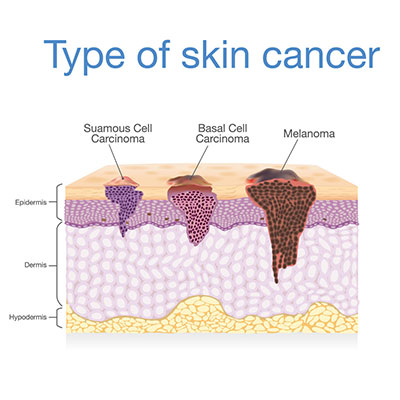
The three main types of skin cancer are the following:
- Basal Cell Carcinoma: the most common type of skin cancer in the world. This type of cancer started at the basal cells. It usually happens at the areas that are exposed to the UV light.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: the type of cancer that started at the squamous cells. The common cause is the over exposure to UV light.
- Melanoma – the most invasive type of skin cancer. It starts at the melanocytes (cells that produce melanin). This type of skin cancer could spread to other organs of the body if left untreated.
Avoiding or reducing the over exposure to the UV light could help reduce the risk in developing skin cancer, sunscreen could also help protect the skin. Skin cancer is most likely to be treated when diagnosed at an early stage.
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of skin cancer are as follows:
- Basal Cell Carcinoma mostly occur at the areas of the skin where it is exposed to the UV lights such as head, neck, arms, hands, and legs.
Basal cell carcinoma signs include:- Shiny pearl-like or waxy bump.
- Skin colored or brown scar-like lesion.
- White, waxy, scar-like lesion without clear border.
- Bleeding or scabbing sores that do not heal.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma mostly seen in sun-exposure areas such as face, ears, and hands. Dark-skin people are more likely to be affected by squamous cell carcinoma even those areas are not over exposed to UV light.
Squamous cell carcinoma signs include:- Firm, red nodule.
- Flat, scaly lesion.
- Open sores
- Thickened or wart – like skin
- Melanoma develops at any areas on the body, it can occur at areas that is not commonly exposed to the UV light.
Melanoma signs include:- Brownish spot with darker patch.
- Lesion that is painful, itchy, or burning sensation.
- Changes at a mole, in color, in size, or bleeding.
If you notice any changes to the skin, and any signs and symptoms, please make an appointment with your doctor.
Causes
Skin cancer occurs when there is a change of DNA in the skin cells. The most common cause of skin cancer is over exposure to the UV light of the sun, and/or tanning beds that damages the DNA of the skin cells which causes abnormal growth of cells that could form into a mass of cancer cells. Exposure to toxic substances or having factors weakening the immune system, could also contribute to the risk.
Risk factors
Factors that may increase skin cancer risk includes:
- Family history – It is highly possible to develop skin cancer if there is a history of cancer from one of your parents or a sibling.
- Overexposure to UV light – people who have over exposure to the UV light of the sun (working or playing) may develop skin cancer, more likely if the person doesn’t use or protected by sunscreen. Excessive usage of tanning beds may also put the person at risk.
- History of sunburn – person who have history of easily sunburnt skin and blisters from sunburn increases the risk of developing skin cancer.
- Tropical or High-altitude climate – people who lived in higher ambient temperature and those who are exposed to UV light are more likely to develop skin cancer.
- Skin color – anyone can get cancer regardless of the skin color. People who have fair skin could provide minimal protection from UV light and is more likely to be at risk of skin cancer.
- Moles – anyone who have many moles or abnormal moles named dysplastic nevi have an increased risk to develop skin cancer. Irregular shaped-moles are higher risk than normal moles, and should be assessed by the physician especially if the mole is bleeding.
- Weak immune system – people who have a weak immune system or are taking immunosuppressant drugs could be at risk.
Diagnosis
If there are changes at your existing mole, or any new abnormal skin growth or skin spots, it is advisable to visit the physician for consultation.
- Skin examination – the specialist will assess the skin for any skin changes.
- Skin biopsy – surgical procedure will be performed by the physician to remove a sample of the abnormal skin for pathology to determine if it is cancer and its type.
- Diagnostic Imaging Procedure – includes Positron Emission Tomography (PET), Computerized Tomography (CT), and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). This is to determine the staging of the cancer.
Once the specialist confirmed the diagnosis of skin cancer, then the following step is to know the staging of the cancer in order to develop a precise treatment plan. The stages of cancer are indicated by Roman numerals ranging from I to IV. The lowest stage indicates a cancer is small and limited. The highest stage – stage IV – indicates that the cancer had spread and advanced.
Treatment
Treatment will depend on the stage of the cancer. The type, size, depth, and location are some of the factors which can effect on how to choose which treatment to apply. Treatment options could be discussed with the specialist.
Biopsy could remove all the cancer tissue if the cancer is small and restricted to the surface of the skin.
Surgery
- Freezing – cryosurgery (freezing with liquid nitrogen) is the treatment that destroy actinic keratoses and some early skin cancers.
- Excisional surgery – removal of the cancerous tissue and the healthy skin that surrounds it, or removal of the tumor.
- Mohs surgery – for the cancer that is large, recurring or difficult to treat. The procedure is to remove the cancerous cells and limit removing the surrounding normal skin tissue. Commonly used for basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas.
- Curettage and electrodesiccation – the specialist will remove the tumor by scraping across it with an instrument and then use a needle in order to destroy the remaining cancer cells. Basal cell and squamous cell cancers are treated best with this method.
Chemotherapy
- Chemotherapy – uses drugs to kill cancer cells. Creams or lotions containing anti-cancer agent will be applied to the top layer of the skin.
Systemic chemotherapy will be used if cancer has spread to other parts of your body.
- Radiation Therapy – an option which is recommended if surgery cannot remove all the cancerous cells.
- Photodynamic therapy – is a treatment that destroys skin cancer cells with a combination of laser light. It help destroy the pre-cancerous cells and avoid destroying the normal cells.





