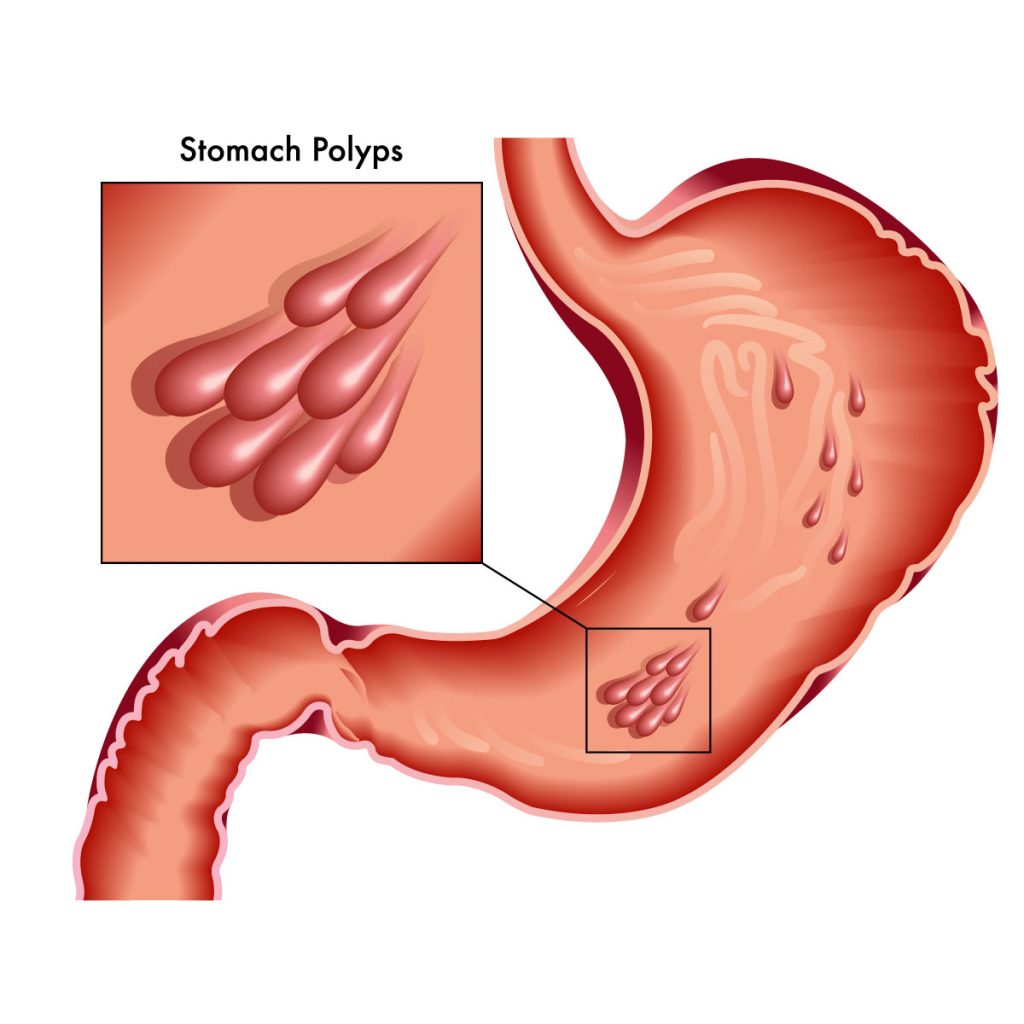
Overview
Stomach polyps form in the stomach lining, known as gastric polyps and they are masses of cells that are not commonly found. Stomach polyps are usually asymptomatic, so, the doctor may only discover them incidentally when the patient seeks consultation for another condition. It does not usually develop into cancer but some types of stomach polyp may put you at risk for stomach cancer. The treatment option for stomach polyp is surgical intervention or just observation for anything unusual that may occur.
Symptoms
Even though a stomach polyp is mostly asymptomatic, when it increases in size, it may develop an ulcer. Furthermore, in a few cases, it may block the opening between the small intestine and the stomach. The following are signs and symptoms that may develop from stomach polyps:
- Nausea
- Pain or tenderness when the stomach is pressed down
- Bloody stool
- Anemia
Consult your doctor if you continue to have a bloody stool or other symptoms which may indicate stomach polyps.
Causes
Injury to stomach lining causes stomach polyps and these are the possible causes:
- Gastritis. Having a chronic inflammation of the stomach can form adenomas and hyperplastic polyps.
- Adenomas are rare types of stomach polyp but can become malignant, so removal is necessary.
- Hyperplastic polyps are the types that are less likely to become malignant if they are less than 1 centimeter.
- Familial adenomatous polyposis. This disorder can be passed on in the family. It makes the cells in the lining of the stomach create numerous polyps. They are mostly removed because they can become malignant. Familial adenomatous polyposis can form adenomas too.
- Regular medication intake. Proton pump inhibitors can cause the formation of fundic gland polyps which are usually small in size and not dangerous. However, if the fundic gland polyps is bigger than 1 centimeter, they carry a risk of developing cancer therefore removal is necessary. Also, stop taking proton pump inhibitors is recommended.
Risk factors
These are the risk factors that may develop stomach polyps:
- Age. Middle-aged adults or older adults are prone to acquire stomach polyps.
- Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) bacterial infection. H. pylori is a bacteria that can be found in the stomach which commonly cause gastritis leading to adenomas and hyperplastic polyps.
- Familial adenomatous polyposis. Having this rare inherited condition puts you at more risk in developing stomach polyps, as well as at risk for colon cancer.
- Taking proton pump inhibitors. Taking proton pump inhibitors to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease for a long time may cause fundic gland polyps.
Diagnosis
These procedures may help to diagnose stomach polyps:
- Endoscopy: Uses a scope to let the doctor see the inside of the stomach.
- Biopsy: A small tissue sample from the stomach is removed while doing endoscopy which is sent to the laboratory for further investigation.
Treatment
The type of stomach polyps will determine the appropriate treatment option such as:
- Small polyps that aren’t adenomas. This type of polyps is usually asymptomatic and has a very low chance of becoming malignant. Treatment is usually not needed but should be observed regularly for any abnormalities.
- Large stomach polyps. This type is removed during endoscopy.
- Adenomas. This type may be removed during endoscopy because they have a higher risk develop into cancer cells.
- Polyps associated with familial adenomatous polyposis. They have a tendency to become malignant so should be removed.
The doctor will recommend endoscope following-up to evaluate for recurring of stomach polyp.
Treating H. pylori infection
Medications which include antibiotics are combined by the doctor to treat gastritis due to H. pylori bacterial infection. The treatment can eliminate hyperplastic polyps and prevent their recurrence.




