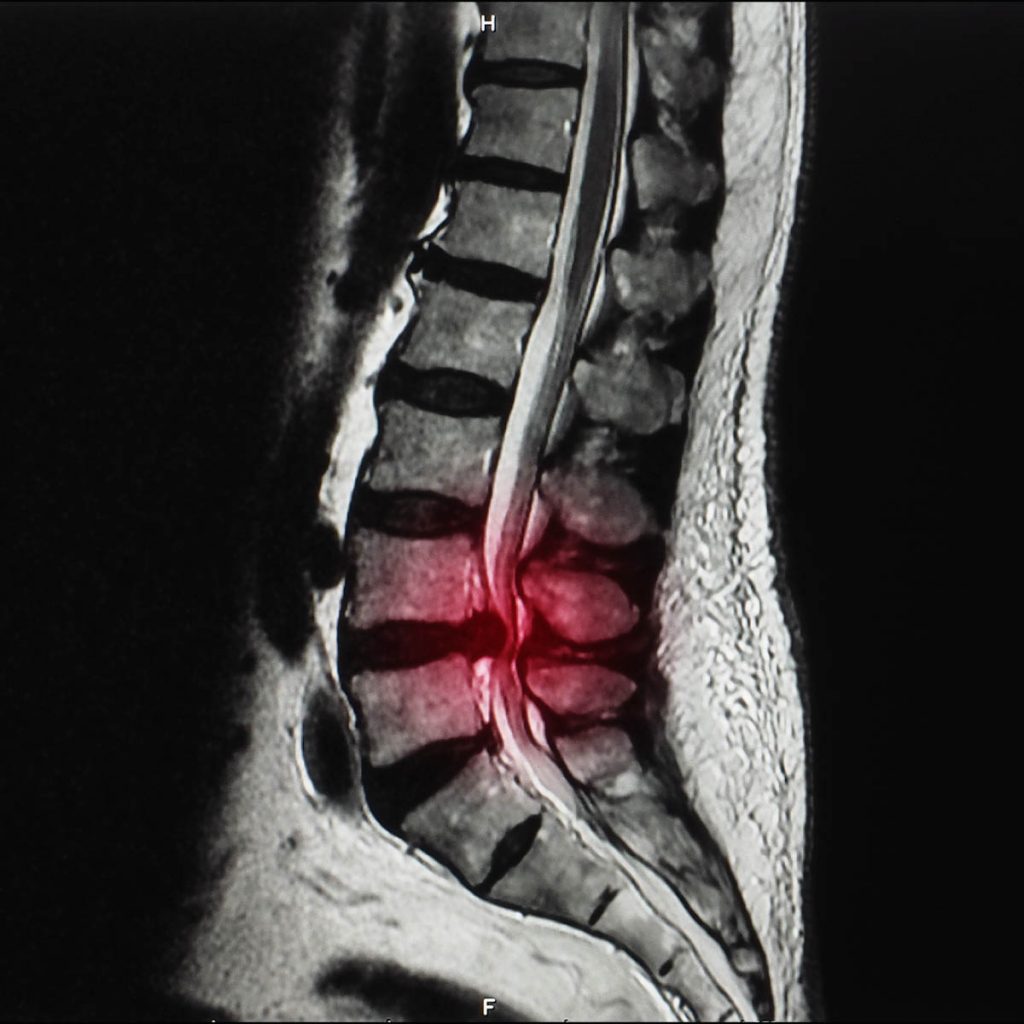
Overview
Spinal stenosis is a condition occurs when the space between the spinal canal becomes narrow caused by wear-and-tear changes due to osteoarthritis. This condition puts pressure on the spinal nerves and commonly occurs in the neck and lower part of the spine.
People over 50 years old are prone to acquiring spinal stenosis but younger people can also have this condition due to birth defect in which the spinal canal is narrow.
Types of spinal stenosis
Spinal stenosis can occur in any part of the spine. There are two main most common types of spinal stenosis based on its location.
- Cervical stenosis. This occurs on the neck area of the spine.
- Lumbar stenosis. This is the most common type and it can be found in the lower back part of the spine.
Symptoms
The signs and symptoms may occur gradually and get more severe as it progresses, the sign and symptom varies on the spot that the nerve has been compressed. A Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) or Computed tomography (CT) Scan can early detect spinal stenosis in patient before they even show up with any signs or symptoms.
Cervical spine
- Pain in the neck
- Upper or lower extremities weakness, numbness or tingling
- Balance and walking problems
- Bowel or bladder (urinary urgency or incontinence) problems in worse cases
Lumbar spine
- Back pain
- Lower extremities numbness, tingling or weakness
- One leg or both experience cramps or pain on prolonged standing or walking. This symptom may be relieved when sitting or bending forward.
Causes
The spine or backbone is located along the neck down to the lower back. The spinal bones create a spinal canal that cushions the spinal cord containing the nerves. There are various causes leading to the spinal spaces to become smaller, although some people can have a narrow spinal canal since birth.
Some of these causes include:
- Bone overgrowth. Osteoarthritis wears down the spinal bones and creates bone spurs that extends into the spinal canal. Certain disease of the bone such as Paget’s diseases (common in adults) can also cause overgrowth of the bones.
- Herniated disks. The vertebrae’s soft cushion dries out upon aging. Then, the disk cracks open and the soft part inside comes out, pressing the spinal nerves.
- Thickened ligaments. The ligament which connects the bones of the spine becomes stiff and thickened, it then protrudes into the canal of the spine.
- Tumors. Tumors or abnormal growths can form in different areas of the spinal cord or vertebrae which can be detected by a CT scan or MRI.
- Injuries of spine. Fractures or dislocation caused by accidents or various traumas can injure the spinal canal. Moreover, after a spinal surgery, nearby tissues can swell and compress the spinal cord or nerves.
- Infection
Diagnosis
The doctor will ask for your signs and symptoms, and your medical history before performing physical assessment. Some tests may also be ordered to properly diagnose spinal stenosis.
Imaging tests
Diagnostic tests include:
- X-rays. Shows bone spurs narrowing the spinal canal and exposing the body to a small amount of radiation.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). This modality shows the damage of disk and ligaments as well as tumors, but mainly, it shows spinal cord or nerves compression. MRI reveals cross-sectional images of the spine using a strong magnetic field and radio waves.
- Computed tomography (CT) Scan or CT myelogram. A CT scan may be ordered by the doctor if MRI is not possible. It is a combination of x-rays from various perspectives to create comprehensive images. CT myelogram on the other hand uses contrast dye injection to outline the spinal cord and nerves, and view bone spurs, tumors or herniated disks.
Treatment
Medications
You may be prescribed the following medications:
- Pain relievers. Pain and discomfort can be managed temporarily by ibuprofen, naproxen and acetaminophen.
- Antidepressants. Chronic pain may be relieved by a tricyclic antidepressant.
- Anti-seizure drugs. Gabapentin and pregabalin may help subside the pain from nerve damage.
- Opioids. Codeine-related ingredient in medications like oxycodone and hydrocodone can be a short-term pain reliever but if they are used in a long-term basis, it should be utilized cautiously due to serious side effects including addiction.
Physical therapy
Immobility caused by pain is very common in spinal stenosis which leads to weakness of the muscles and create more pain. Physical therapists may teach you to exercises in order to regain or improve your endurance, strength, flexibility, stability and balance.
Steroid injections
Steroid injection helps to subside pain and inflammation but it will not fix the spinal stenosis. Furthermore, once used repeatedly, it can make the bones and connective tissues weak.
Surgery
When other treatments have failed, surgery is the next option. Surgery is done to relieve pressure on the spinal cord and nerves. This can be achieved by making more space inside the spinal canal. An experienced spinal surgeon for spinal stenosis should be considered in order to have less chance of complications.
Spinal stenosis can be surgically corrected through these techniques:
- Laminectomy. Removes the damaged lamina (back part) of the vertebra. It is sometimes called decompression surgery because it releases the nerves from pressure and makes more space in the spinal canal. Metal hardware and bone graft can be used to combine the vertebrae to make it stronger in some patients.
- Laminotomy. Only a tiny part of the lamina is taken out which creates a small hole releasing the pressure at a certain area.
- Laminoplasty. Only done in the neck’s vertebrae (cervical spine) creating space in the spinal canal by making a hook to the lamina. Metal hardware fills the space in the spine’s open spots.
- Minimally invasive surgery. Removes the bone or lamina without creating injury to the normal tissues surrounding it. This procedure will less likely need fusion.
- Endoscopic decompress. Use endoscope to decompress neural element
- Microscopic decompression. Use microscope to decompress
Spinal fusion may stabilize the spine and alleviate the pain but there is also more chance of pain and inflammation after the surgery or damage in areas surrounding the spine. Minimally invasive surgery is more favorable due to a much lesser time needed to attain recovery.