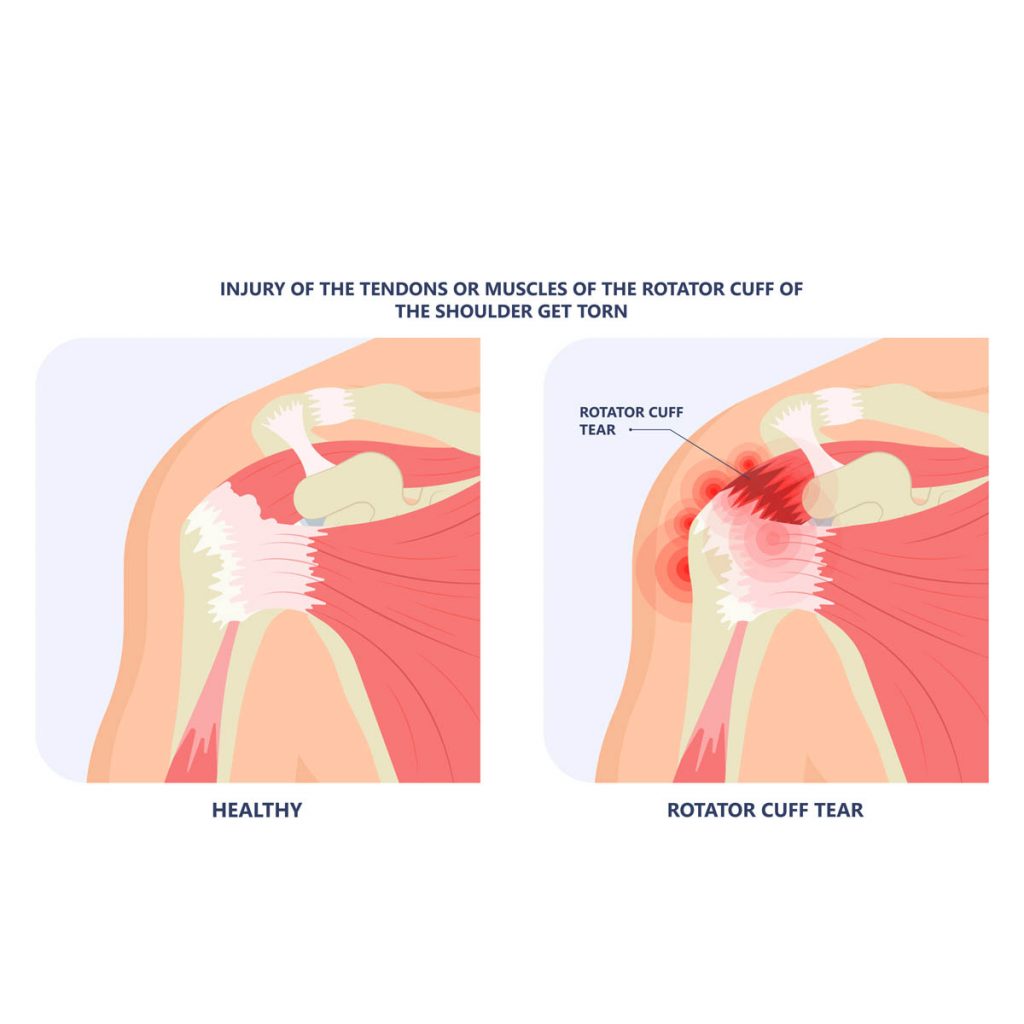
Overview
Rotator cuff consists of many muscles and tendons around the shoulder which plays a major role in shoulder movements. Rotator cuff Injury can be encountered in people who use their shoulder repetitively over time and even more common in some occupation where the shoulder are over used (e.g., painters or carpenters). It is more common as you get older (more than 60 years old) and it may be caused by a history of injured shoulder. Some familial traits are more prone to getting this type of condition. Mainly, the cause of rotator cuff injury are from degeneration or overuse.
Symptoms
The sign of rotator cuff injury are:
- Weakness around the shoulder
- Sleeping disturbance
- Deep dull shoulder pain
- Recurrent pain with specific activities
- Cracking sound upon shoulder movement
- Difficulty in doing simple tasks such as reaching your back or combing your hair
If you experience sudden shoulder or arm weakness, consult the doctor immediately.
Diagnosis
Doctor will perform physical examination to see any signs of injury, these includes performing specific test, strength test and checking the range of motion of the shoulder. Furthermore, these investigations may also be recommended:
- X-rays. Detects any fractured bone or other factors causing pain but it cannot show the rotator cuff tear.
- Ultrasound. Shows images of the soft tissues and tendons by using sound waves.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). Views overall shoulder structures in a higher definition using sound waves and a strong magnetic field.
Treatment
The symptoms can usually resolve on its own in some people by conservative treatment such as resting the affected area, cold compression and physical rehabilitation or exercises. But, if the damage is extreme, surgery may be indicated.
Injections
Steroid injection may be indicated to reduce the shoulder pain if conservative treatment fails. Moreover, the use of this injection should be use only short term because it can weaken the tendon and can stop the progress of the surgical procedure later on.
Physical Therapy
Initial treatment for rotator cuff injury is a customized physical therapy to assist in regaining the shoulder’s muscle strength and range of motion.
Surgery
Various type of surgical interventions are available, such as:
- Arthroscopic tendon repair. Reconnects the tendon to the bone which is done arthroscopically (using a tiny tube with a camera) by creating a tiny incision around the shoulder.
- Open tendon repair. A larger incision is done to repair the damage and reconnects the tendon to the bone which is a better option in some case.
- Tendon transfer. A nearby tendon can be utilized if the damage to the tendon is too vast and it is impossible to connect it to the bone.
- Shoulder replacement. An artificial joint replaces the widely damaged rotator cuff. This procedure is also called a reverse shoulder arthroplasty to stabilize the shoulder.
Lifestyle and home remedies
Try to rest and avoid using your shoulder from strenuous activities which can increase stress to your rotator cuff. Home remedies may include taking over-the-counter pain-relief medications (e.g. ibuprofen or acetaminophen) and cold compression. In most cases, people can manage the symptoms of rotator cuff injury together with physical rehabilitation which will improve muscle strength and range of motion.