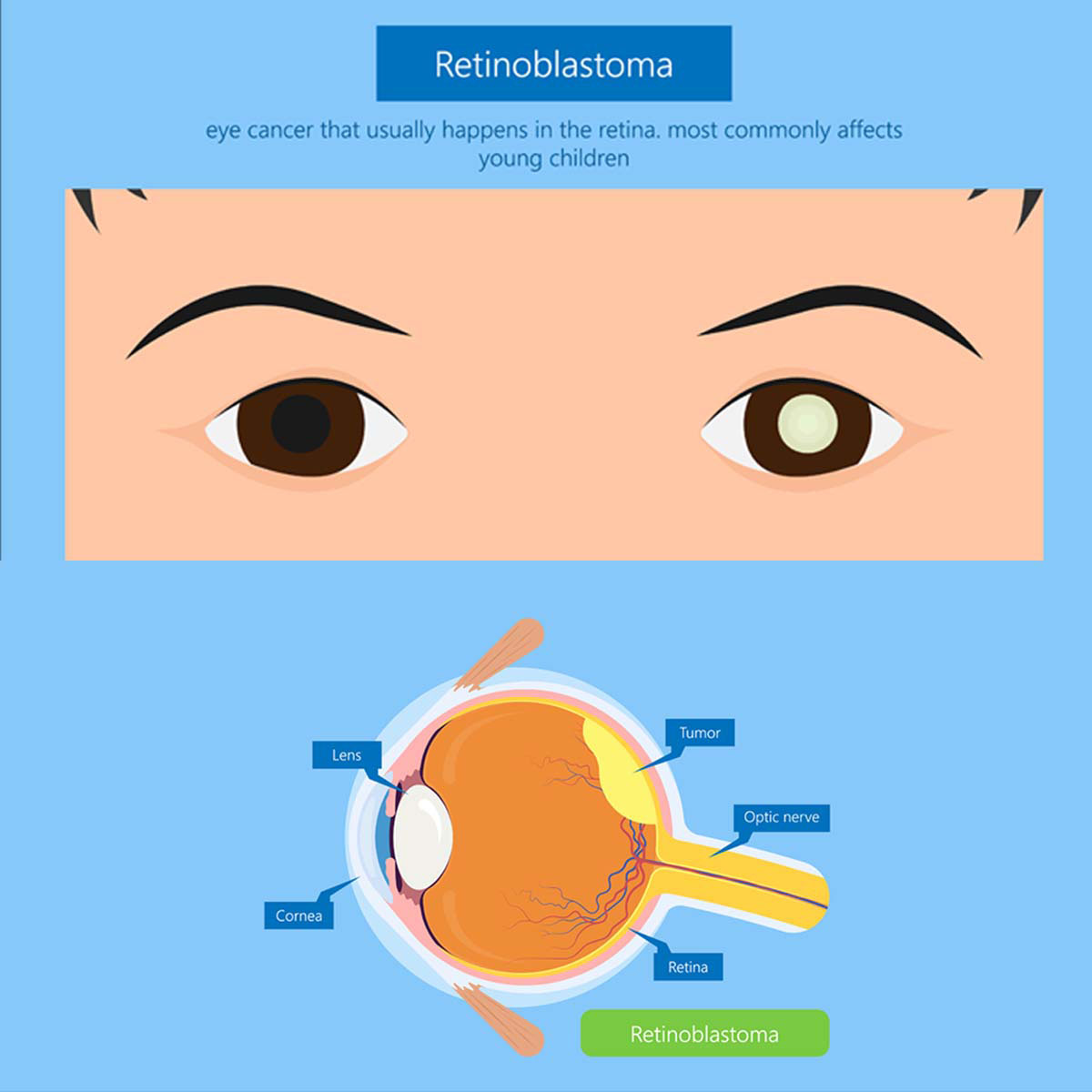
Overview
The retina is located at the back of the eye. It contains cells that detects light and gives information to the brain that creates images. Retinoblastoma is a rare type of eye cancer that affects the retina and it is mostly found in young children. Adults rarely have this condition and it may affect only one or both eyes.
Causes
The cause of retinoblastoma is by a genetic mutation of the retina’s nerve cells which leads to rapid growth of the abnormal cells and later on forms a tumor. It may affect other structures of the eye or even spread to other parts of the body (metastasize) if untreated
It is unclear what causes the genetic changes leading to retinoblastoma but it is can possibly be passed on by the parents to their children.
Inherited Retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma that is inherited has an autosomal dominant pattern where only one parent has one copy of the genetic mutation to pass on to the child. The probability of inherited retinoblastoma is 50% in each child even if only one parent carries the gene that has mutations occurring in one or both eyes.
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms are not common because retinoblastoma often occurs in infants and young children. You may watch out for the following signs:
- Crossed eyes (strabismus)
- Vision problems
- Eye redness or swelling
- Leukocoria (white or cloudy pupil) is observed on direct flashing of light (e.g., when taking a photograph of a child)
When you notice these symptoms, consult the doctor.
Diagnosis
The following tests may be done to detect retinoblastoma:
- Eye exam. The doctor will perform eye exam to determine the cause of the signs and symptoms.
- Imaging studies. To see whether retinoblastoma has spread to other structures around the eye. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan and ultrasound creates more detailed images of the eyes.
- Spinal tap. Checks for the presence of cancer cells in the spinal fluid.
- Bone marrow biopsy. May determine if the cancer has spread into the bones and bone marrow.
Treatment
Treatment for retinoblastoma is based on the tumor’s size, location, and if the cancer has spread to other structures of the eye. The parent’s treatment choice and the overall health of the child is also taken into consideration.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses medications that kill cancer cells of retinoblastoma.
- Intravenous chemotherapy.
- Intra–arterial chemotherapy. Injecting drugs into the tumor through a catheter in an artery supplying blood to the eye.
- Chemotherapy injected directly into the eye.
Radiation therapy
Uses high–powered energy, such as X–rays and protons to eradicate cancer cells. It can be done locally (plaque radiotherapy or brachytherapy) to treat retinoblastoma or using an external beam radiation.
Laser therapy (transpupillary thermotherapy)
Heat laser may be directly applied to the tumor to destroy tumor cells.
Cold treatment (cryotherapy)
Using a very cold substance such as liquid nitrogen to repeatedly freeze and thaw cancer cells which leaves them to die.
Eye removal surgery
Surgery is done if the tumor is too huge and other treatments are not helpful. It is also done to avoid the spread of cancer to other areas of the body. The following techniques may be performed:
- Enucleation. Removes the affected eyeball including the optic nerves.
- Eye implant. Done after enucleation and replaces it with a special ball into the eye socket.
- Fitting an artificial eye. Artificial eye (usually artificially customized) may be inserted on top of the eye implant and it sits at the back of the eyelid.
Surgery may affect the other eye’s vision but the child can usually adapt. Special eyeglasses (shatter–resistant or goggles for sports) may be used for eye protection.




