Overview
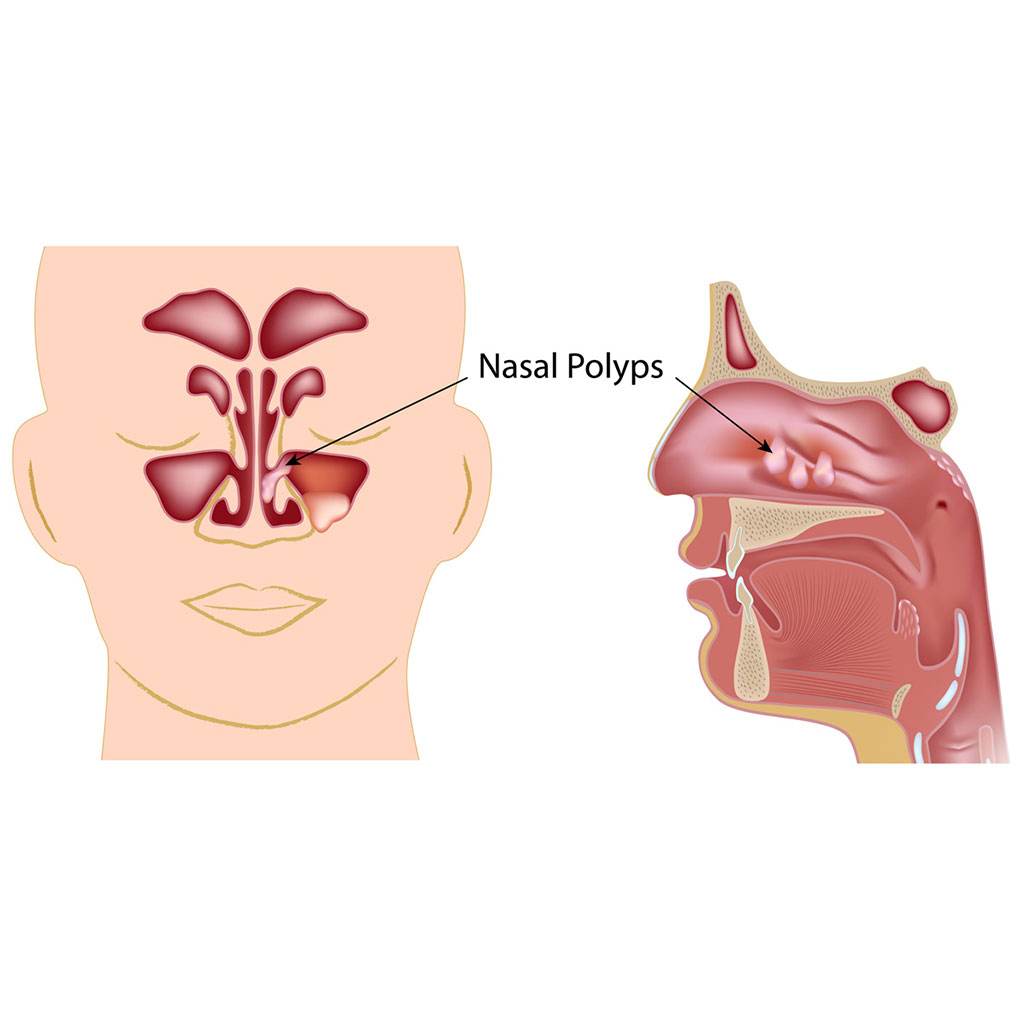
Nasal polyps are noncancerous lesions arising from the mucosa of the nose and sinus. Nasal polyps are more common in adults, although they can also occur at any age. They look like dangling teardrops which are soft but do not cause pain. Chronic inflammation causes nasal polyp to occur which is related to having recurring infection, allergies, asthma, immune disorders, or drug sensitivity.
Although no symptoms arise from nasal polyps but in large quantities, they may cause blocked nose or breathing difficulties, infections that keep recurring, and loss of sense of smell.
Treatments includes medication that can decrease size of the nasal polyp or remove it. However, surgery may be required. Nasal polyps can be eliminated, but there is also a tendency for them to recur.
Symptoms
Chronic irritation and inflammation of the nasal pathway and sinuses (chronic sinusitis) causes nasal polyps. Although nasal polyps can occur without having chronic sinusitis.
If the nasal polyps are small, they may be unnoticeable. However, large, or numerous nasal polyps can cause blockage of the nose and sinuses.
Nasal polyps and chronic sinusitis have these common signs and symptoms.
- Nasal congestion
- A runny nose or postnasal drip
- Loss of sense of smell
- Loss of sense of taste
- Headache or facial pain
- Upper teeth pain
- Frequent nosebleeds
- Snoring
If these symptoms last for more than 10 days, consult your doctor. There are many diseases which have symptoms that are almost the same with nasal polyps or chronic sinusitis.
Call for emergency medical assistance right away if you experience these symptoms:
- Severely swollen eyes
- Difficulty of breathing
- Sudden worsening of symptoms
- Double vision or limited eye movement.
- Intense headache with high fever or not being able to move your head forward.
Causes
The causes of nasal polyps are unclear. Nasal polyps are associated with long-term inflammation of the nasal passage and sinuses but not all cases are caused by nasal inflammation. There are some evidences that the people who develop nasal polyps tend to have a unique immune response and mucous membrane chemical markers based in the lining of the nose and sinus.
Nasal polyps commonly occur in young and middle-aged adults, although they can occur at any age. The most common areas where nasal polyps occur are in the sinuses near the nose, eyes and cheekbones. However, they may occur in any parts of the sinuses or nasal pathways.
Risk factors
The risk of having nasal polyps increase due to some triggers that causes irritation and inflammation of the sinuses and nasal passages (e.g., allergies and infections).
The following conditions are related to acquiring nasal polyps:
- Aspirin sensitivity
- Asthma. This condition constricts the airways.
- Allergic fungal sinusitis, airborne fungi allergy
- Cystic fibrosis. This is a genetic disease that causes the body fluids to become sticky which causes the nose and sinuses linings to secrete thick mucus.
- Churg-Strauss syndrome (eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis). This is a rare disorder which causes the blood vessels to become inflamed.
- Vitamin D deficiency.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of the doctor is usually symptoms-based together with assessment of the nose and the whole body. A polyp may be seen by flashing a light into it.
Some tests which may be done to diagnose nasal polyps which include:
- Nasal endoscopy. A nasal endoscope is a tiny tube with a magnifying lens and a lighted camera which is used by the doctor to have a better view of the nasal passages and sinuses.
- Imaging studies. Computerized Tomography (CT) scan can view the size of the polyp and its location inside the sinuses and as well as assess how swollen and inflamed the polyps are.
The imaging will assist the doctor to check for other blockages in the nasal passages (e.g., unusual structures or other growths which may be benign or malignant)
- Allergy tests. Skin prick test done on the skin of the forearm or upper back may be performed by the doctor to know what your allergies are that cause chronic inflammation. Blood tests may also be done to check for certain antibodies of different allergens.
- Test for cystic fibrosis. A test for cystic fibrosis called noninvasive sweat test may be recommended by the doctor if your child has been found to have nasal polyps. Cystic fibrosis is a disorder that is passed on by the family (hereditary) which affects the glands that secrete sweat, tears, saliva, mucus, and digestive fluids. Noninvasive sweat test determines if the sweat of a child has an above average salt concentration.
- Blood test. Nasal polyps may be caused by a deficiency of vitamin D levels in the blood.
Treatment
It is quite difficult to eliminate chronic sinusitis with or without polyps. You will have to carefully plan the long-term treatment with your healthcare providers to help ease your symptoms and to treat risk factors such as chronic inflammation and allergies.
Nasal polyp treatment aims to shrink the nasal polyp or fully remove them. The first line of treatment is by using medications. Surgery may be recommended in some cases but it’s not a treatment that lasts because nasal polyps mostly recur.
Medications
The initial treatment for nasal polyps is medication that can reduce the size of the polyps or totally eliminate it. These medications include:
- Nasal corticosteroids. A nasal corticosteroid will be prescribed by the doctor to alleviate symptoms such as irritation and swelling. Furthermore, this treatment can reduce the size of the nasal polyps or totally make them disappear. Budesonide, mometasone, ciclesonide, fluticasone, beclomethasone, and triamcinolone are examples of nasal corticosteroids.
- Corticosteroids. Medication taken orally may be prescribed by the doctor if nasal corticosteroid is not effective such as prednisone administered together with the nasal spray. However, oral corticosteroid has serious side effects, hence they are only taken short-term. In the case that the nasal polyp has become serious, corticosteroid may be administered intravenously.
- Medication for nasal polyps and chronic sinusitis. An intravenous medication such as dupilumab may be administered by the doctor if you have nasal polyps and chronic sinusitis to alleviate nasal congestion and help shrink the nasal polyp.
- Other medications. If you have allergies that promotes swelling in your nasal passages and sinuses for a long time, the doctor may recommend medications such as antihistamines for the allergies and also an antibiotic to resolve the chronic infection or an infection that keeps coming back.
An allergy doctor may also recommend aspirin desensitization treatment which can help treat nasal polyps and sensitivity to aspirin. In this procedure, the doctor slowly adds more dosage of aspirin while the patient is admitted at a clinic or hospital to create a long-term tolerance to aspirin.
Surgery
Endoscopic surgery is an outpatient procedure which uses a tiny tube with a lighted camera (endoscope) to reach for the nasal passages and sinus cavities. A surgical instrument can also be inserted into the endoscope to access the polyps and remove them as well as other blockages in the sinuses.
The surgery does not only remove the nasal polyps, but it also assists in treating sinuses inflammation and prevent further polyp growth as well as widen the pathway from the sinuses down to the nasal passages.
A saline rinse will be prescribed by the surgeon after the surgery to induce healing. Furthermore, a corticosteroid nasal spray is then applied post-surgery in order to avoid the nasal polyps from recurring.




