Overview
Melanoma is a form of cancer that occurs in the cells that contributes to the production of melanin, which is a substance that creates pigmentation to skin and eyes. Ocular melanoma is another term for eye melanoma. Eye melanomas occur in the region of the eye that cannot be seen by making it difficult to detect the disease. No signs or symptoms appear in the early stage of eye melanoma. The vision may not be affected by the treatment procedure for some small eye melanomas, however for large ones, there is a chance of vision loss when undergoing treatment.
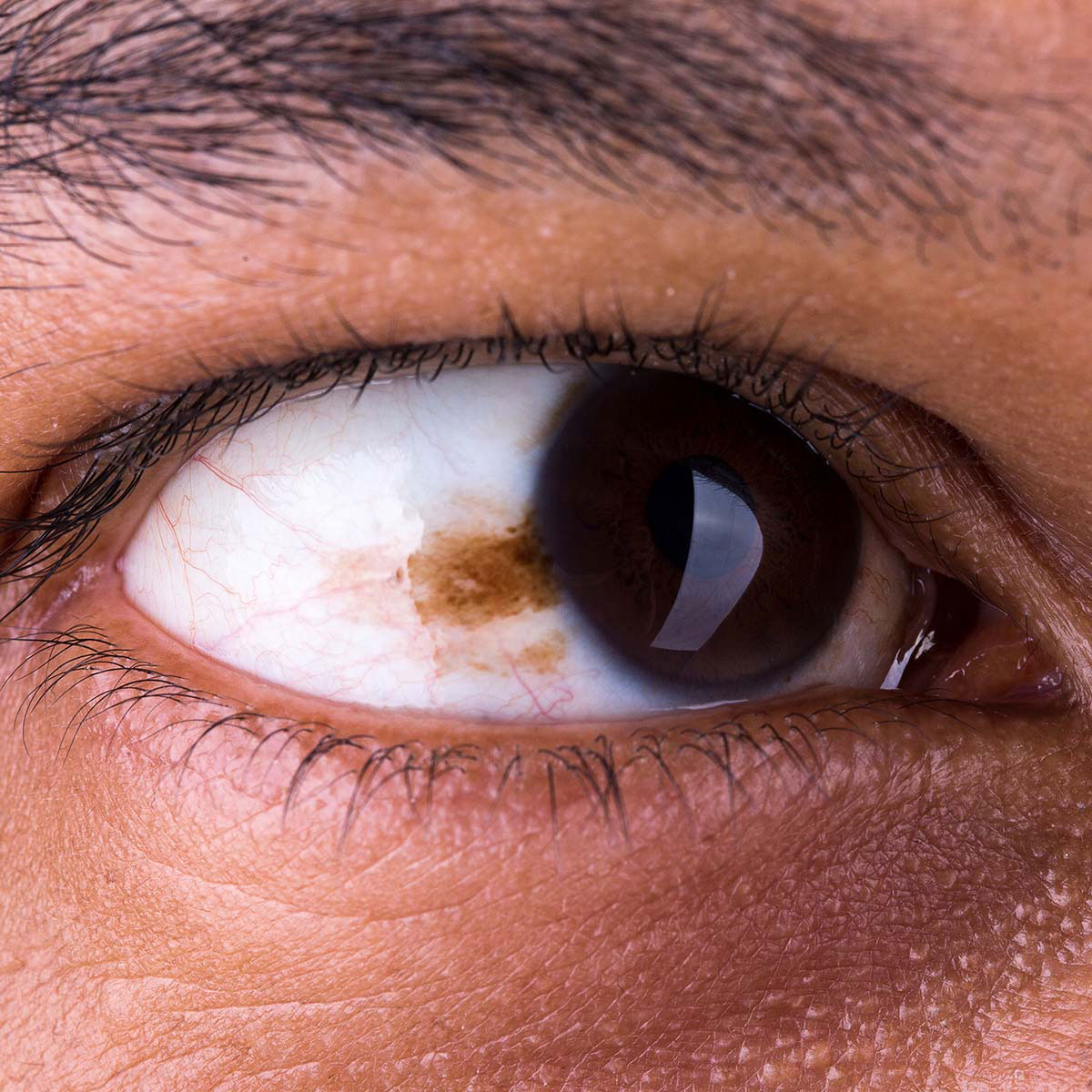
Symptoms
- Flashes or specks of dust in the vision or eye floaters
- A dark spot growing on the iris
- Changing of shape of the pupil in the eye
- Blurry or poor vision in one eye
- Loss of peripheral vision
If you experience any of the above symptoms, consult a doctor. Seeking immediate medical care is recommended if you have sudden vision changes.
Causes
The reason behind the development of eye melanoma is unclear. Eye melanoma can be detected when some errors arise in the DNA of healthy cells in the eye. The errors that occurs in the DNA cause the cells to grow and multiply themselves without a control. This makes the mutated cells to continue living when normally they are supposed to die. The accumulation of the mutated cells in the eye turns into an eye melanoma.
Eye melanoma development:
Eye melanoma generally occurs in uvea, which is the cells in the middle layer of the eye. The uvea composed of three parts. Eye melanoma can have an effect on each of them:
- The iris: the colored area in the front of the eye
- The choroid layer: the layer of blood vessels and connective tissue located in the middle of the sclera and the retina.
- The ciliary body: in the front of the uvea, it releases the transparent fluid or aqueous humor into the eye
Aside from these three areas, eye melanoma can arise around the outer layer on the front of the eye known as conjunctiva, or in the socket surrounded by the eyeball and on the eyelid. However, these types of eye melanoma are uncommon.
Risk factors
- Light eye color: Blue- or green-eyed people are at a higher risk of developing eye melanoma.
- White people: White people are more likely to have eye melanoma.
- Age: With increase of age.
- Some inherited skin disorder: Dysplastic nevus syndrome holds the possibility of developing eye or skin melanoma. People with ocular melanocytosis have an increased risk of eye melanoma.
- Being exposed to ultraviolet light: Exposure to UV light, such as sunlight or light from tanning beds may increase risk of the disease.
- Genetic mutations: Particular genes passed down to children from parents may raises the possibility of developing eye melanoma.
Diagnosis
- Eye examination: The outside of the eye will be examined for enlarged blood vessels, to check for tumors.
- Eye ultrasound: is the use of high-frequency sound waves that come from a transducer to create images of the eye.
- Angiogram: is an imaging of the blood vessels located inside and around the tumor. This procedure requires an injection of a colored dye into a vein in the arm to be distributed to the blood vessels in the eye. A special filtered camera that is used to detect the dye captures flash images.
- Optical coherence tomography: is an imaging test that produce photos of a part of the uveal tract and retina.
- Biopsy: A procedure done by inserting a thin needle into the eye to collect a tissue sample. The tissue sample will be sent to the laboratory to check for eye melanoma cells.
Determining metastasis:
- Blood test: liver function tests
- Chest X-ray
- Abdominal ultrasound
- Computerized tomography (CT) scan
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan
- Positron emission tomography (PET) scan
Treatment
The proper treatment options that will be used to treat the disease, depend on the location and size of the eye melanoma. If the condition of eye melanoma is small and not growing, immediate treatment may not be necessary. Treatment could be received, if melanoma grows or leads to complications.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy is the implementation of powerful energy beam, such as protons or gamma rays, to kill cancer cells. When melanomas are small or medium, radiation therapy could be used to treat the disease.
- Brachytherapy. This is the procedure of delivering radiation to the tumor. A radioactive plaque is placed on the eye, directly on top of the tumor. The plaque is attached with temporary stitches so it stays in place for four to five days before its removal.
- External beam radiation, or teletherapy.
Laser treatment
In certain cases, laser treatment can be used to kill the melanoma cells. Thermotherapy, is a form of treatment that requires an infrared laser and it can be used in combination with radiation therapy for some cases.
Photodynamic therapy
Photodynamic therapy is the combination of medications and a special wavelength of light. The cancer cells become vulnerable to light because of the medications. Then the vessels and cells result in eye melanoma are destroyed. However, this type of therapy is effective in small melanoma and does not help to treat larger cancers.
Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy (cold treatments) is extreme cold treatment that kills melanoma cells that contain in certain small eye melanomas. Nevertheless, this treatment is not generally used.
Surgery
Operations include the removal of a part or the entire eye depending on the size and location of the eye melanoma.
- Surgical removal of the melanoma and a small part of healthy tissue around the melanoma could be an option to treat small melanomas.
- Enucleation: is the surgical procedure to remove the entire eye. Typically used for large tumors developed in the eye. This treatment option is also considered when the tumor is causing pain in the eye.
After the removal of eye melanoma, an implant will be placed in the same position to replace the eye. The muscles that are responsible for controlling eye movement will be connected to the implant so it can move. Once the healing period is over, an artificial eye or prosthesis will be placed. The front surface of the prosthetic eye will be painted to match the real existing eye of the patient.





