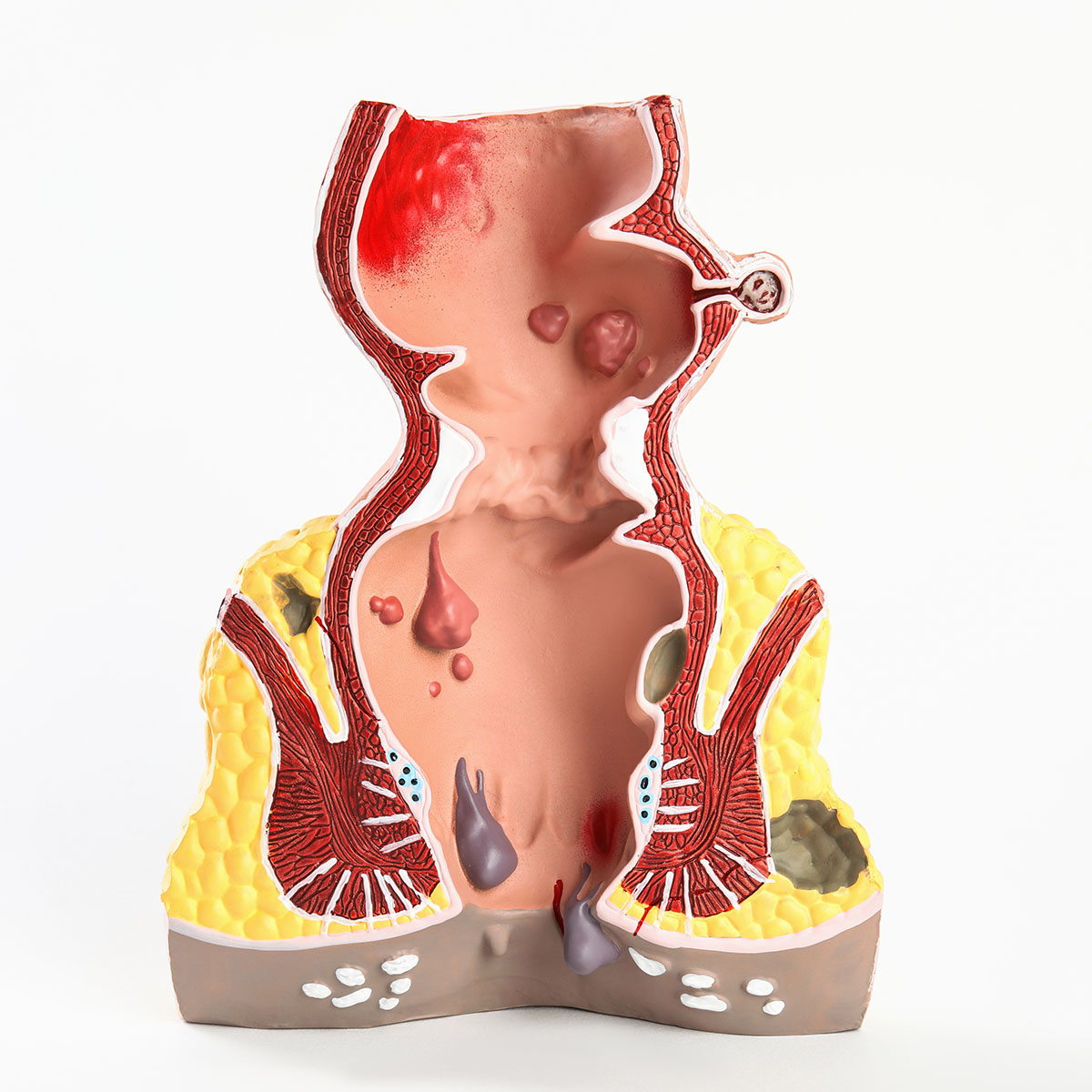
Overview
Anal cancer is a cancer that start in the anus which is the end part of the rectum. It is the final short tube (about 2 to 4 cm long) of the rectum where the stool leaves the body.
Anal cancer is a rare type of cancer that affects the anal canal and skin around the anus. It is also called carcinoma of the anal canal and margin.
The treatment of anal cancer includes surgery, chemotherapy and radiation.
Symptoms
The following are the signs and symptoms of anal cancer.
- Anal or bleeding
- Mass in anal canal
- Having pain at the anus
- Itchiness at the anus
- Incontinence of stool
- Inconsistent bowel movement
If you notice these symptoms, consult your doctor.
Causes
The cause of anal cancer starts with the mutation of the genes which can turn healthy cells into abnormal cells. It instructs the abnormal cells to divide rapidly outgrowing the healthy cells and creating a tumor. After some time, cancer cells may spread to the surrounding tissues or other parts of the body (metastasis).
Anal cancer is more common with those who have high risk subtypes of human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, which is a sexually transmitted disease, IV infection, receptive anal intercourse.
Risk factors
These factors have higher risk of having anal cancer:
- Multiple sexual partners
- Anal sex (receptive)
- Having HPV infection (high risk subtypes 16,18)
- Old age. 50 years old or older.
- Women are more at risk than men. However, men who have sexual intercourse with men are also at higher risk.
- HIV infection
- History of cancer. Having a history of cervical, vulvar or vaginal cancer
- Drugs or conditions that suppress your immune system. Taking immunosuppressant medications for those who have had organ transplants. HIV infection which suppresses the immune function.
- Smoking
Diagnosis
The following tests are performed to diagnose anal cancer:
- Precancerous lesion:
- Anal Pap smear combined with anoscopy.
- Risk subtype test: can be followed up upon the risk of cancer to be prevented.
- Cancerous:
- Digital rectal examination. To examine the anal canal and rectum, doctor will insert a gloved finger with lubrication inside the rectum to palpate for any abnormalities.
- Visual exam with anoscopy. An anoscope (a short tube with light) is utilized by the doctor to inspect the anal canal and rectum for any abnormalities.
- Ultrasound of the anal canal. A small probe is inserted into the anal canal and rectum which uses sound waves to create images of the tissues or organs to check for abnormalities.
- Biopsy. A small sample of the tissue from the part with abnormalities is sent to a lab for testing under a microscope to check for cancer cells.
Determining the extent of the cancer
Other tests may be recommended by the doctor once there is a final diagnosis such as to check if the cancer has affected the lymph nodes or has spread to other parts of the body. These tests are as follows:
- Computerized Tomography (CT)
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
The results will determine the stage of anal cancer which ranges from 0 to IV (Roman numerals). The lowest stage means that the cancer is small and localized in the anus. At stage IV, it means that the cancer has spread to other parts of the body. The doctor uses staging to determine which treatment to apply.
Treatment
The treatment is based on the stage of anal cancer, general health of the patient and the patient’s treatment of choice and location of disease.
Combined chemotherapy and radiation (Predominantly use)
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy are combined to have a higher chance for successful treatment.
- Chemotherapy. Uses medications which are taken orally or intravenously to kill cancer cells.
- Radiation therapy. High-powered beams by x-rays and protons are utilized to destroy cancer cells in specific areas of the body.
Surgery
- Role of surgery:
- If the cancer is T1 (<2 cm lesion)
- Recurrent or persistent of lesion
Different techniques are utilized by the doctors to remove anal cancer depending on the stage as follows:
- Surgery for early-stage anal cancers. The tumor is removed along with some healthy tissues around it if the size is small. In this case the anal sphincter that controls bowel movement may not be destroyed. Chemotherapy and radiation may also be done after the surgery.
- Abdominoperineal resection for persistent or recurrent lesion (APR).A broader surgery called abdominoperineal resection may be done if the tumor is not responsive to chemotherapy and radiation. This technique removes the anal canal, rectum and a part of the colon. The part of the colon that is left is attached to a stoma (opening of the abdomen) where waste products leave the body and collected into a colostomy bag.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy may be applied in advanced cancer stage. This treatment kills cancer cells using your own immune system. Cancer cells release proteins that shield themselves from the body’s disease-fighting immune response. Immunotherapy destroys this process to kill the cancer cells.





