Overview
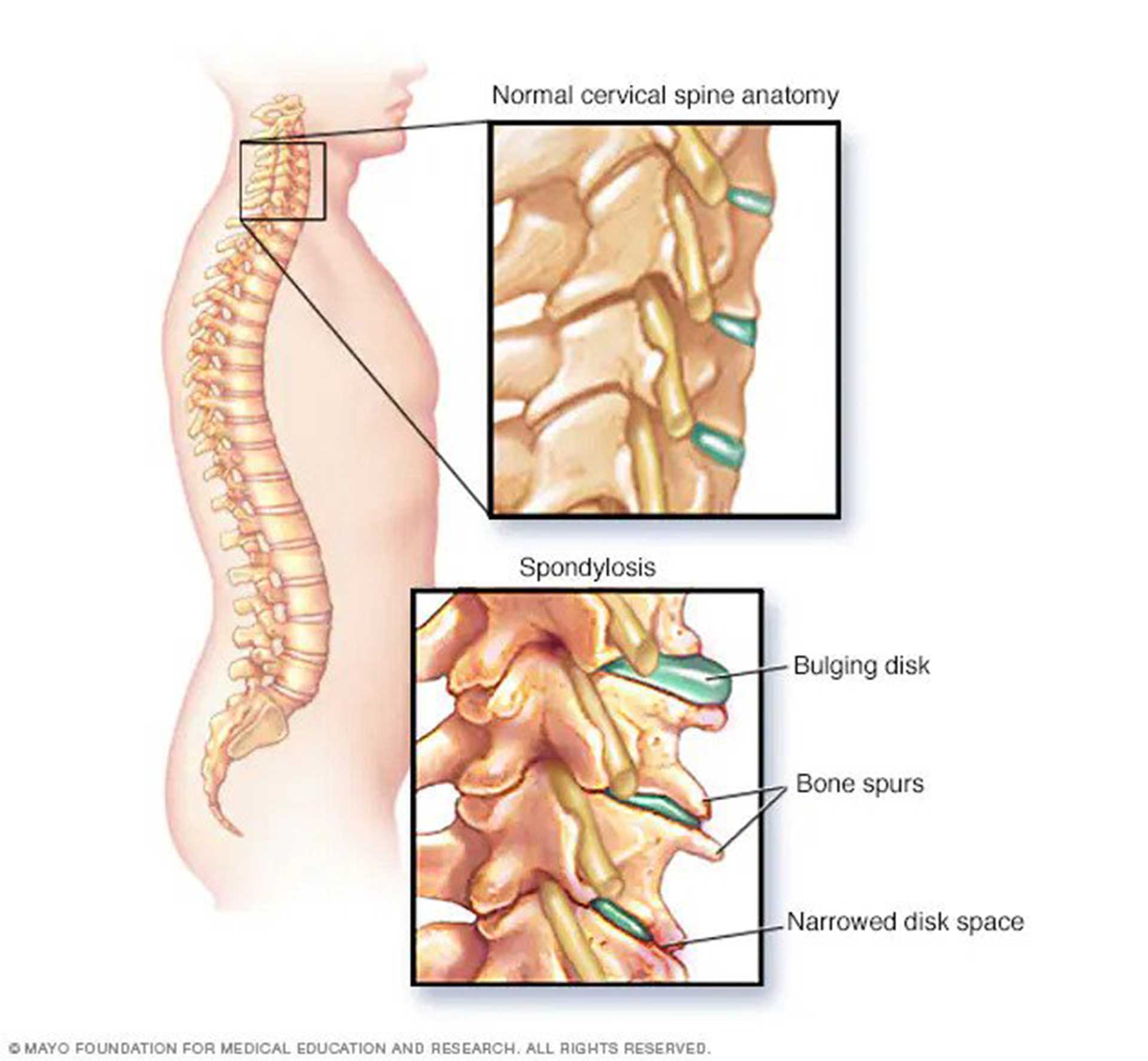
Cervical spondylosis is the wearing down of the spinal disk in the neck due to dehydration and shrinkage. This condition may occur as you age, mostly in people who are more than 60 years old. Osteoporosis and bone spurs then develops later on.
Symptoms
Cervical spondylosis can be asymptomatic but if symptoms occur, stiffness and pain usually manifests.
The spinal cord and nerve roots are inside a space passing across the spine. When this space is narrowed as a result of cervical spondylosis, it compresses the spinal cord and nerve roots, and you will notice the following signs and symptoms.
- Weakness, numbness or tingling sensation on upper and lower extremities
- Walking and coordination problem
- Bladder and bowel incontinence
These are the symptoms that you will have to observe because you may need to see a doctor immediately.
Causes
The bones of the back and neck are prone to degeneration as you get older and the following changes may be observed:
- Dehydrated disks. The spinal disk’s role is to become the cushion in between the vertebrae. When it becomes dry or shrinks starting at around 40 years of age, the bones of the spine will be rubbing against each other.
- Herniated disks. When the spinal disk’s outer layer cracks open, the disk bulges out and puts on pressure on the spinal nerves and cord. This condition is called a herniated disk.
- Bone spurs. The spine has a tendency to produce additional bone structures as a defense mechanism to make the spine stronger due to degeneration creating bone spurs that can compress the spinal nerve roots and spinal cord.
- Stiff ligaments. Ligaments connects the bones with each other. When they become stiff due to aging, it affects the flexibility of the neck.
Risk factors
These are the risk factors for cervical spondylosis:
- Neck injuries
- Age. Old age mostly leads to cervical spondylosis.
- Occupation. Working conditions which provides a lot of pressure on the neck or repeatedly uses the neck.
- Genetic factors. Cervical spondylosis can be hereditary
- Smoking. Aggravates the pain.
Diagnosis
A physical assessment will be performed by the doctor to check your reflexes, your neck’s motion range and check how you walk to find out if there are any signs of spinal cord and nerve compression.
Imaging tests
- X-ray. A neck X-ray can detect bone spurs and other factors causing pain and stiffness in the neck (e.g., fracture, infection, or tumors)
- Computed Tomography (CT) scan. Shows a more detailed image of the bones.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). Shows any nerve compression.
- Myelography. Gives a clearer X-ray and CT scan image by injecting a dye in the spinal canal.
Nerve function tests
The following are the types of nerve function tests to check for any damage to the nerves.
- Electromyography.Shows muscle contraction and relaxation which receives command based on the electrical conduction in your nerves.
- Nerve conduction study. A mild electrical shock is delivered through electrodes attached on the skin where the nerves are to assess the nerve’s electrical conduction.
Treatment
Cervical spondylosis is treated to alleviate the pain, stop further spinal cord and nerve damage, and help you get back to your normal tasks. The treatment is based on how serious are the signs and symptoms.
Medications
The following medications are prescribed if over-the-counter drugs cannot manage the symptoms.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs). Prescription–strength medications may be more helpful for the pain and inflammation other than using over-the-counter drugs.
- Corticosteroids. Prednisone as an oral medicine may help alleviate the pain but if it’s still not enough, steroid injection is another option.
- Muscle relaxants. Cyclobenzaprine is a drug specifically prescribed to relieve neck muscle spasm.
- Anti-seizure medications. Gabapentin and pregabalin are anti-seizure medications but they also dull the nerves to prevent pain sensation.
- Antidepressants. Neck pain can also be relieved with the help of some antidepressant medications.
Physical Therapy
You will be taught with some neck and shoulder muscle stretching and strengthening exercises by the physical therapist. Traction also helps create space and relieve compression on the nerves of the spine.
Surgery
You may have to undergo surgery if you manifest signs of severe arms or legs weakness. The goal of the surgery is to provide space for the nerve roots and spinal cord. The procedure will involve removing parts of the vertebra, herniated disk or bone spurs; and utilize a bone graft or hardware to combine parts of the neck.




