Overview
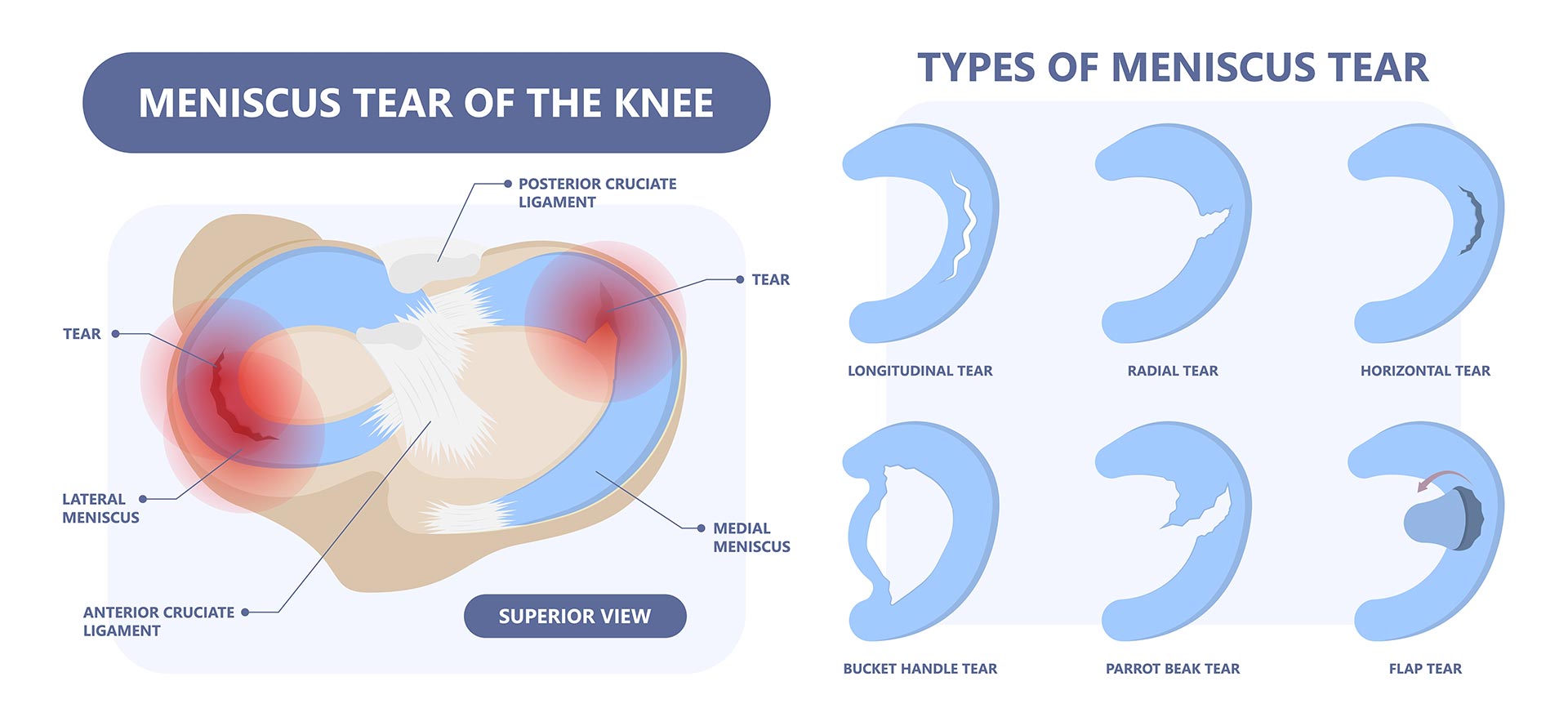
The meniscus is a flexible crescent-shaped cartilage between the thighbone and shinbone that provides a cushion that absorbs and disperses attack or pressure as a result of walking, running or jumping. The meniscus is usually an injury due to the force of twisting or rotating the knee.
A torn meniscus or meniscus tear is characterized by knee pain, swelling and stiffness. Limitation of knee motion can be felt and there can also be a difficulty with full knee extension.
Symptoms
It may take 24 hours for the pain and swelling to develop after acquiring a torn meniscus. The following symptoms on your knee may also be observed:
- Pain during knee movement
- Swelling
- A popping sound during the occurrence of injury
- Stiffness
- Inability to fully bend or straighten the knee
- Feeling of unstable knee
When you can no longer move your knee as usual, or your knee is painful or swelling, you should get medical care for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Causes
Athletes of certain contact sports (e.g., football, tennis or basketball) are more prone to a torn meniscus due to forceful pivoting or instantly pausing and twisting of the knee. Moreover, some activities such as squatting, kneeling or lifting heavy weights can also lead to this condition. In older people, degenerative arthritis can cause a tear without a knee injury.
Diagnosis
The doctor will perform a physical examination and move your knee in a certain motion to assess for any signs of torn meniscus.
Imaging tests
- X-rays. Because meniscus won’t show up in the X-rays, the test can help evaluating other knee problems which can also cause the symptoms.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). The doctor will investigate patient’s condition by doing MRI scan, to specifically evaluate the knee structures including tendon, muscle, meniscus and articular cartilage.
Arthroscopy
The doctor may recommend knee arthroscopy to accurately diagnose knee injury. This can be done by a small incision and inserting a small camera to inspect the meniscus injury.
Treatment
Conservative treatment could be typically solved and surgery is not automatically suggested for a torn meniscus, especially if it is due to arthritis or other conditions that are not related to locked knee or a knee-blocking movement. The pain just lessens over time. The treatment depends on the tear’s type, size and location.
Using over-the-counter pain relievers and following the RICE protocol can help reduce knee pain and swelling.
- Resting
- Ice pack on your knee for about 20 minutes, several times a day
- Knee compression bandage to reduce swelling.
- Elevating the leg higher than the heart also helps to reduce swelling. (2)
Physical Therapy
You will be able to regain your knee and leg muscle strength and stability with proper physical therapy
Surgery
When non-operative treatments have failed, the doctor may recommend a surgery. A torn meniscus can often be repaired in children and young adults. In case surgery is considered necessary, the doctor may introduce meniscus repair, an arthroscopic procedure that cause less damage to the muscles and nearby organs. Through very small incisions (1 centimeter) as portals, a surgeon inserts camera attached to the arthroscope which displays injured area then uses special surgical instruments to fix the torn meniscus.
Patients are managed by using axillary crutches for 1 month to lessen the pressure sent to the meniscus and allow its natural healing process. After that, they are encouraged to go through rehabilitation to improve mobilization and strengthen the muscle and ligaments to finally go back to normal activities.





