A Warning Sign from the Heart: Why Persistent Fatigue Shouldn’t Be Ignored
Feeling fatigued easily may be an early sign of heart disease. Learn how fatigue links to heart failure, heart arrhythmia, cardiomyopathy, and more.
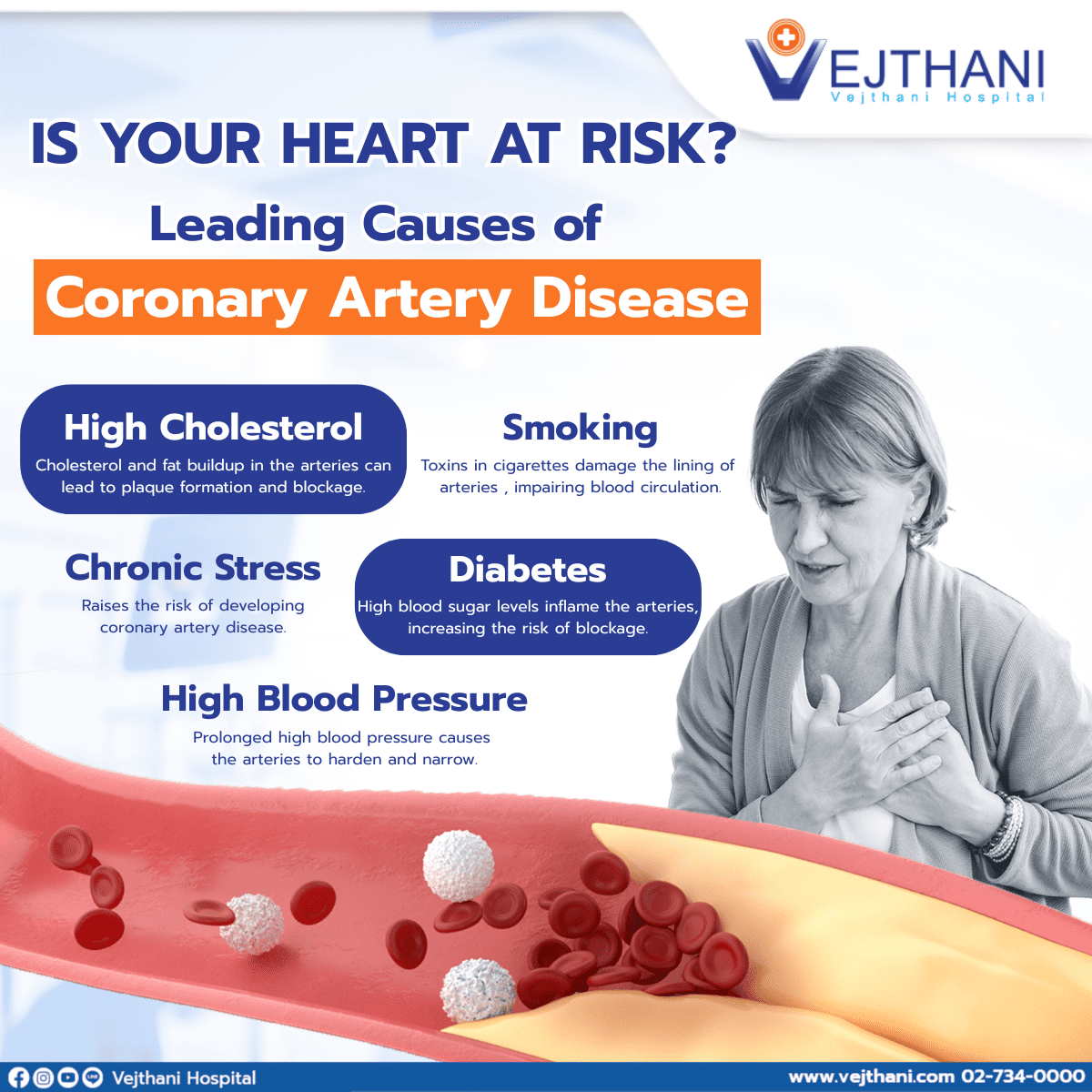
Coronary artery disease is one of the leading causes of death worldwide. This critical condition occurs when the coronary arteries become narrowed or blocked, restricting blood flow and reducing the supply of oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle. The narrowing or blockage is typically caused by a buildup of fatty or calcium deposits inside the arteries.
Coronary artery disease may lead to ischemic heart disease and heart failure if not properly treated. Key risk factors include:
If you have any of these risk factors, do not ignore them. Coronary artery disease often shows no symptoms until it reaches an advanced stage. Common warning signs include chest pain or tightness in the center of the chest (just above the upper abdomen), pain radiating to the left shoulder or arm, fatigue, weakness, heart palpitations, excessive sweating, and dizziness.
If you experience any of these symptoms, seek medical attention promptly. The best approach is to prioritize your health on a regular basis: avoid high-fat foods, exercise regularly, manage stress, and undergo comprehensive heart health screenings.
Remember, your heart is one of the body’s most vital organs—and good health starts with a strong heart.
Cardiac Center, Vejthani Hospital
Call: (+66)2-734-0000 Ext. 5300
English Hotline: (+66)85-223-8888
