Health Articles
Stent with Balloon Angioplasty for Heart Disease Treatment
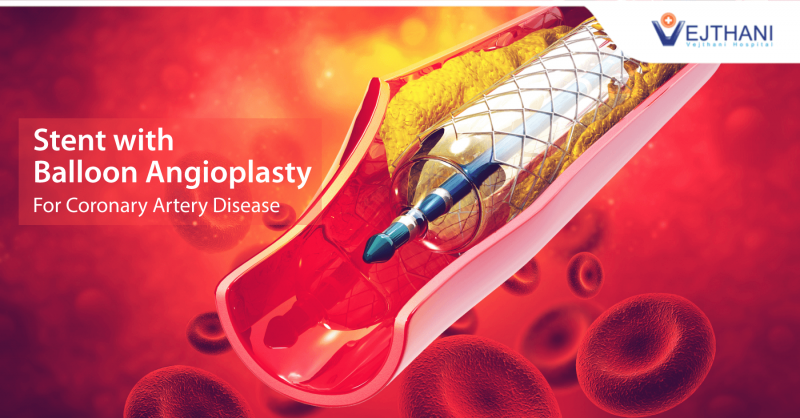

Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is generally a result of a condition known as atherosclerosis in which a waxy plaque forms inside the arteries that supply blood to the heart, thereby narrowing them and making blood flow to the heart difficult. With deteriorating blockage, the flow of blood to heart slows down leading to a condition known as angina that makes us vulnerable to a heart attack. The pain caused by angina can be treated with medication, however it cannot remove plaque from the blocked arteries. Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) with balloon angioplasty or a stent is an option to clear the blocked arteries.
What is a Stent?
Stents are tiny mesh-like tubes made from stainless steel. They are placed permanently inside an artery (blood vessel) to hold it open after a balloon angioplasty (PTCA).
The actual procedure for placement of the stent is the same as an angioplasty with the addition of the stent placement.
Why is a Stent used?
A stent may be used to keep an artery open that has closed or partially closed after a previous angioplasty (ies) to improve the flow of blood.
In some cases, stents are used when blocked bypass vein grafts are opened through angioplasty.
How is a Stent placed?
- First, an angioplasty is done to open the blockage in the area.
- After the artery is opened, a catheter, which has a stent over a deflated balloon on the tip, is reinserted into the artery up to the area previously opened by angioplasty.
- Once in place, the balloon is inflated, expanding the stent and pressing it against the artery wall.
- The balloon is deflated and the catheter and balloon are removed, but the stent remains expanded and in place to help keep the narrowed portion open after angioplasty.
- The stent will remain in the artery permanently.
- The artery will heal around the stent.
- The procedure lasts for one to two hours.
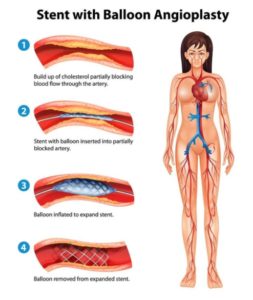

Fig. 01: An Illustration of Stent with Balloon Angioplasty Procedure
What symptoms may be experienced during the procedure?
- A slight burning or stinging from the medicine used to numb the catheter insertion site
- A slight discomfort or pressure as the catheter is being inserted
- Slight nausea and/or extra heartbeats
- Chest pain may occur as the balloon catheter is being inflated, but it is temporary
What happens after the procedure is completed?
- After X-rays are taken, the balloon and catheter are removed.
- The sheath (IV) is usually left in place in the leg overnight until the blood thinning medications are discontinued and clotting time returns to normal.
- A band aid or pressure dressing will be placed over the area where the catheter was inserted.
- The patient will be admitted to a special cardiac care unit (CCU) to be closely observed.
- When the sheath is removed from the groin, (usually the following day), firm pressure is applied to the sheath insertion site for 15-30 minutes until the bleeding stops.
- If an artery in the arm is used, pressure will be applied over sheath insertion site for 15-30 minutes.
- The insertion site will be checked frequently for signs of bleeding.
- Blood pressure and the pulse in the leg (or arm) used will be checked frequently.
- A knot under the skin where the catheter was inserted may occur. This is only temporary.
- Bruising to the leg/groin area may occur where the catheter was inserted. The bruising may spread down the leg and is only temporary.
- Most patients are discharged in eight hours with minimal activity restrictions.
What precautions should be taken following the procedure?
- Avoid bending the leg at the hip (groin area) for six to eight hours after the catheter is removed.
- Hold the band aid firmly if it is necessary to cough or sneeze.
- Avoid bending or using the arm for six to eight hours if it was used for the insertion of the catheter.
Cardiologists at Vejthani Cardiac Center specialize in the treatments of coronary #artery disease, valvular heart disease, angina pectoris or chest pain and acute myocardial infarction or heart attack. Our physicians also treat patients requiring interventional non-invasive cardiac imaging.
For appointments & inquiries, please contact:
Vejthani Cardiac Center, 5th Floor,
Vejthani Hospital
Phone: +66 (0) 2734-0000 Ext. 5300, 5301
Email: [email protected]