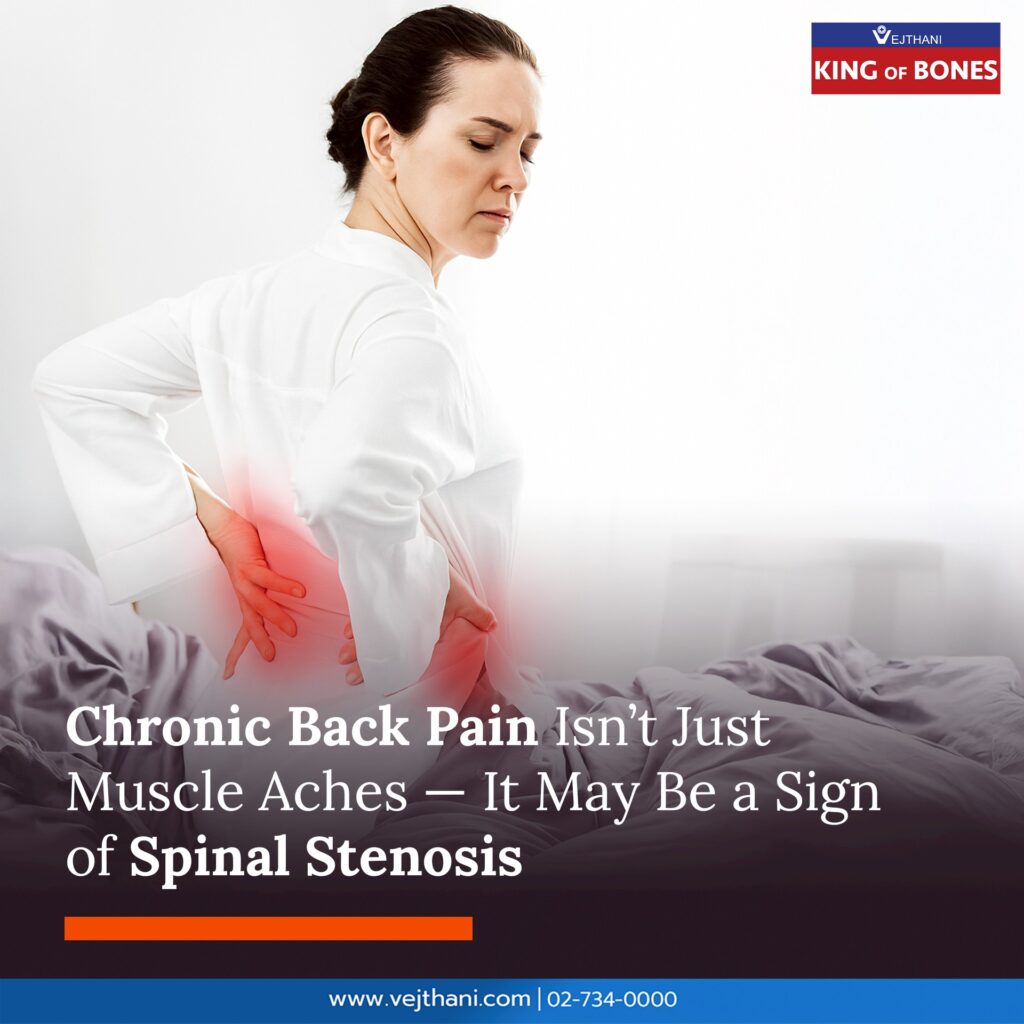
Many people downplay chronic back or neck pain, assuming it is a minor issue that will resolve on its own. However, these symptoms may be an early warning sign of a herniated disc, a condition that, if left untreated, can worsen and significantly impact your daily life.
What is Herniated Disc?
A herniated disc occurs when one of the spinal discs—responsible for absorbing shock and allowing smooth movement—tears or slips out of place. This displacement can press on nearby nerves, causing pain, numbness, or weakness in various parts of the body, such as the back, neck, hips, or legs.
Symptoms of Herniated Disc
Symptoms vary depending on the location of the disc herniation and the degree of nerve compression. Common signs include:
- Chronic back or neck pain, especially during movement or heavy lifting
- Radiating pain along the nerve path (e.g., down the leg if the disc slips in the lower back, or down the arm if in the neck)
- Numbness or weakness in the legs, arms, or hands
- Electric shock-like sensations when moving or staying in certain positions
- Muscle weakness or limited range of motion
If left untreated, symptoms can worsen over time and may lead to:
- Muscle atrophy or increasing weakness
- More intense nerve pain and numbness
- Loss of bowel or bladder control in severe cases
Causes of Herniated Disc
- Age (typically affects those between 30 to 50 years old)
- Poor posture or improper use of the spine (e.g., lifting heavy objects incorrectly)
- Spinal injury or trauma
- Excess body weight or obesity
- Lack of regular exercise causes weak back muscles
Diagnosing Herniated Disc
Diagnosis typically begins with a medical history and physical examination. Additional tests may include:
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): A detailed scan to detect nerve compression and assess the severity of disc damage.
Treatment Options
For mild or early-stage herniation:
- Pain relief medications
- Physical therapy
- Lifestyle adjustments, such as correcting posture and modifying sleeping or lifting habits
For more severe or persistent symptoms:
If the condition does not improve within six months or becomes more severe, such as radiating leg pain, sleep disturbances, difficulty walking, or loss of bladder/bowel control, your doctor may recommend endoscopic discectomy, a minimally invasive spine surgery.
Benefits of Endoscopic Discectomy
- Small incision (around 1 cm)
- Minimal trauma to surrounding tissue, resulting in less post-operative pain
- Faster recovery time and quicker return to daily activities
Preventing Herniated Discs
While age-related degeneration cannot be entirely avoided, you can lower your risk and delay the onset of symptoms by:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Exercising regularly to strengthen core and back muscles
- Avoiding smoking
- Having a balanced diet
- Practicing proper posture when sitting, standing, bending, or lifting
- Changing your position regularly when working at a desk
- Taking precautions to avoid spine-related injuries
Don’t Ignore Chronic Pain
If you’ve been experiencing persistent back pain, neck pain, or numbness in your limbs, don’t wait for it to become more severe. Consult a spine specialist for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment recommendations.
For more information, contact
Spine Center, Vejthani International Hospital
Tel: 02-734-0000 ext. 5500
English Hotline: (+66)85-223-8888