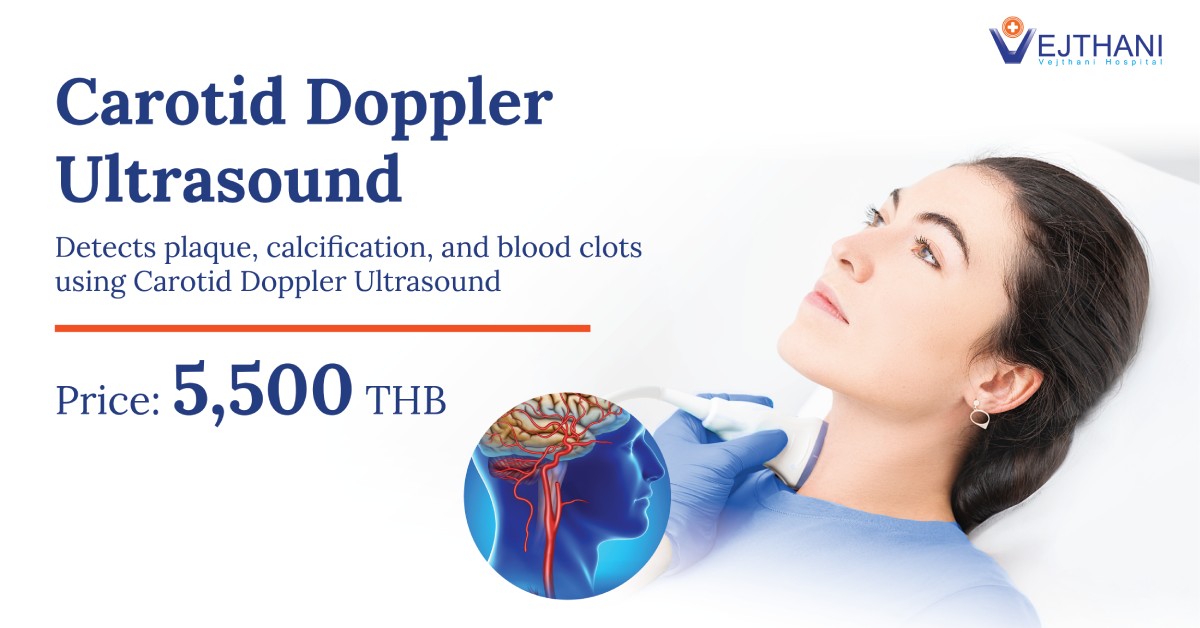
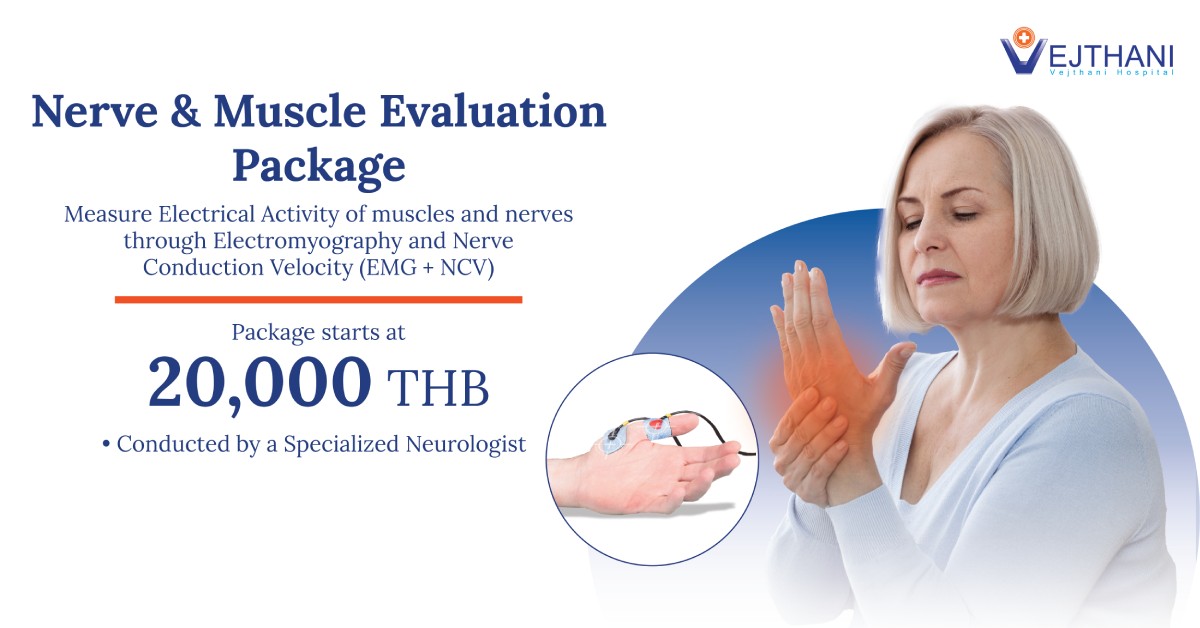
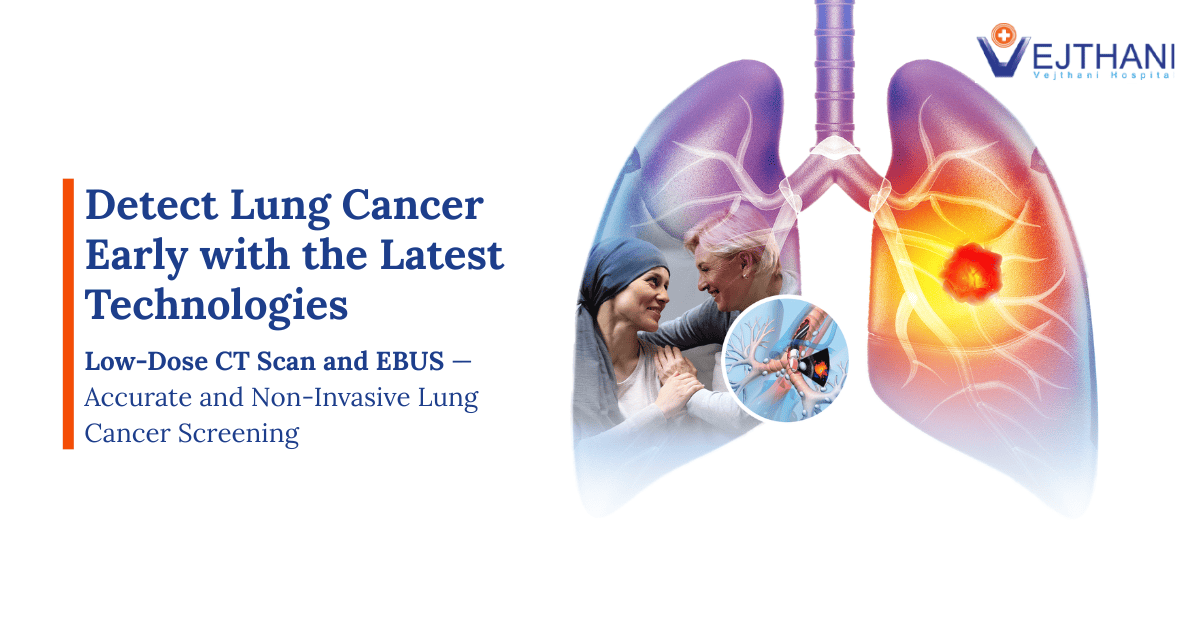
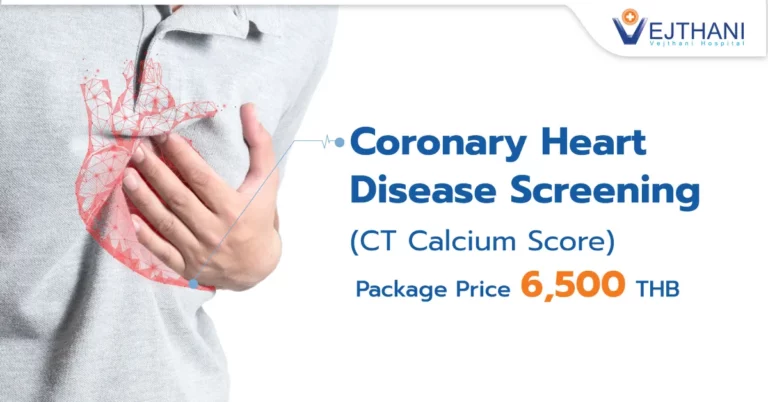
Find out before it’s too late! Even if you are physically fit, sudden cardiac arrest death could happen unknowingly to anyone during exercise from undetected coronary artery disease (CAD).
We have surely heard of many incidents about the deaths of runners and athletes caused by acute cardiac arrest and heart attack appeared in the news. Fifty percent of this group of people were clueless that they had coronary artery disease.
Dr. Zaida Buranasin, Cardiologist at Vejthani Hospital has revealed that 80% of athletes over 35 years old whom have died of heart attack had Coronary Artery Disease (CAD). Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is caused by buildup plaques made up of excess calcium or cholesterol in the walls of arteries resulting in the inside of the arteries to narrow over time and eventually create a blockage of blood flow. Worse case is when plaques rupture, it can lead to a blood clot in the artery causes the patients to have chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath or even severe symptom that results in a heart attack.
“Symptoms of acute coronary artery disease may become more prominent when the heart pounds rapidly causing it to work harder to pump more blood through your body. For instance, exercising or doing daily activities can cause your heart to beat faster than usual. When climbing up the stairs, during sexual intercourse, heavy lifting, when you are surprised or stunned, or even after working out, you may experience acute coronary artery disease. Hence, screening tests for cardiovascular disease is considered as the best preventive measure”, said Dr. Zaida.
Abnormalities in your coronary arteries before exercise can be detected by the following tests:
- Exercise Stress Test or EST: Measures your heart rate or its ability to respond to external stress while you walk on a treadmill. However, abnormality cannot be detected through this test if there is a mild narrowing inside the walls or a slight blockage of the arteries and the blood flow is still good.
- Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography (CCTA): An imaging test that is used to scan the coronary arteries for calcium buildup and plaque. Cardiologists may consider doing this test on people who are at high risk of having coronary artery disease. For example, those who have over 10% heart score of EGAT or have a family history of coronary artery disease or have high level of fats in their blood as well as people who are into heavy workout.
For people who are at high risk of having coronary artery disease, the cardiologist may consider ordering more tests as follow:
- Coronary artery calcium scoring: Calculate the risk of coronary artery disease with the help of a CT Scan by measuring the amount of calcified plaque in the blood vessels. If the result scores over 400, the patient has a chance to have coronary artery disease within the next 2 – 5 years.
- Cardiac Catheterization Angiography (CAG): Is a minimally invasive imaging procedure that examines the inside of your arteries for narrowing or blockage by inserting a catheter into the blood vessel around the groin, arm or neck area to reach the heart, then injects the radiopaque contrast agent into the coronary arteries. The cardiologist will perform the stent and balloon angioplasty as soon as the narrowed coronary arteries were detected.
Screening to detect the abnormality of coronary artery disease among athletes is therefore crucial as hidden coronary syndrome can become symptomatic and leads to death especially for people who are overly fond of high- intensity exercise. For example, before running a marathon or triathlon, it is essential to consult a specialist to determine the fitness and the strength of the heart as well as the body. If symptoms of coronary artery stenosis occur, doctors will treat the patient in accordance with the severity of the disease. Treatments may include the intake of Anticoagulants, or antiplatelets or undergoing Angioplasty and stent implantation along with making adjustments or changes to life style and follow suitable exercise routine. Simply adhering to these recommendations will reduce the risk of acute coronary artery constriction.
Nevertheless, if anyone experience a sudden cardiac arrest or a heart attack, CPR or Cardiopulmonary resuscitation should be performed within 4 minutes to increase the chance of the patient’s survival.
For more information, please contact
Cardiac Center, 5th floor, Vejthani Hospital
Call: (+66)2-734-0000 Ext. 5300
English Hotline: (+66)85-223-8888
- Readers Rating
- Rated 5 stars
5 / 5 ( Reviewers) - Spectacular
- Your Rating