As the peak viral season is approaching, the infections are drawing closer to your children playgrounds and loved ones. But the good news is they can be easily prevented. Hand Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD) is one of the regional endemic viral infections that especially affects the children. Thai health officials have issued advisory about the disease several times. Through this health advisory we have answered the common questions about HFMD.
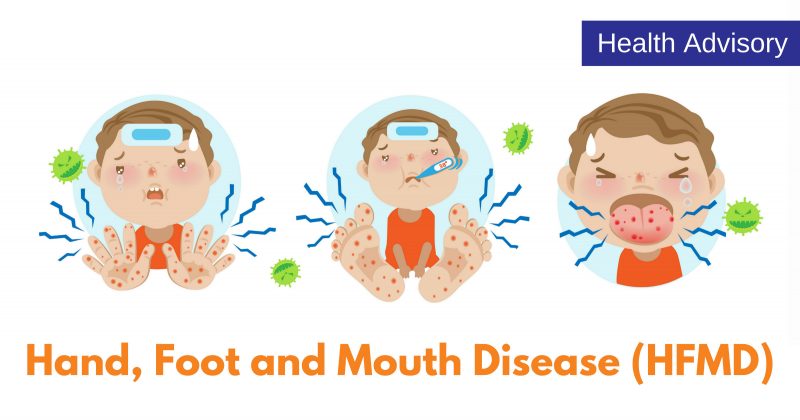
HFMD is mostly seen in infants and children under the age of five, is a viral disease that generally starts with a fever, sore throat, loss of appetite and a general feeling of tiredness. These initial symptoms are followed by painful sores in the mouth, and rashes of flat red spots that may blister on the palms, soles, fingers, and sometimes the knees, elbows, buttocks, and/or genital area within a few days that usually last for a week.
Oral lesions form because of the blistering of tiny red spots in the mouth affecting the buccal mucosa, gums, palate and tongue. The lesions make it difficult for children to swallow liquids and hence they may get dehydrated.
However, HFMD may not manifest any symptoms at all in some individuals, especially adults. Despite that, the infected adults can still transmit the disease to others.
Viruses from the group called enteroviruses cause HFMD. There are many different types in the group including polioviruses, coxsackieviruses, echoviruses and other enteroviruses. HFMD is most commonly caused by coxsackievirus A16 which usually results in a mild self-limiting disease with few complications. However, in Southeast Asia, Enterovirus 71 generally causes HFMD outbreaks that can lead to life-threatening complications including encephalitis, aseptic meningitis, polio-like flaccid paralysis, pulmonary hemorrhage and myocarditis. Most fatalities are implicated to pulmonary hemorrhage or edema.
When someone gets HFMD, they develop immunity (protection) to the specific virus that caused their infection. However, because HFMD is caused by several different viruses, people can get the disease again.
The most effective preventive measure for HFMD is practicing good hygiene. You can reduce the risk of getting infected with the viruses that cause HFMD by following a few simple steps:
- Wash your hands often with soap and water for 20 seconds, especially after changing diapers, and help young children do the same.
- Avoid touching your eyes, nose, and mouth with unwashed hands.
- Avoid close contact such as kissing, hugging, and sharing cups and eating utensils with people who have HFMD.
- Disinfect frequently touched surfaces and objects, such as toys and doorknobs, especially if someone is sick.
There is no treatment or vaccination against HFMD. It is important for people with HFMD to drink enough fluids to prevent dehydration.
Especially if you suspect HFMD in your kids, please visit our 24-hours dedicated Super Kids Center specialists who often go out of their way to offer personalized medical advice including the up-to-date tips on how to deal with the diseases like HFMD, medical intervention and patient care. The center offers a complete range of pediatric sub-specialties associated with primary prevention and treatment to complex medical interventions including NICU, Cardiology, Allergies, Orthopedics, Congenital Diseases and so on. We are fully prepared to meet the preventive, diagnostic and treatment needs of your children.
- Readers Rating
- Rated 4.8 stars
4.8 / 5 ( Reviewers) - Spectacular
- Your Rating