
Rheumatoid arthritis

Overview
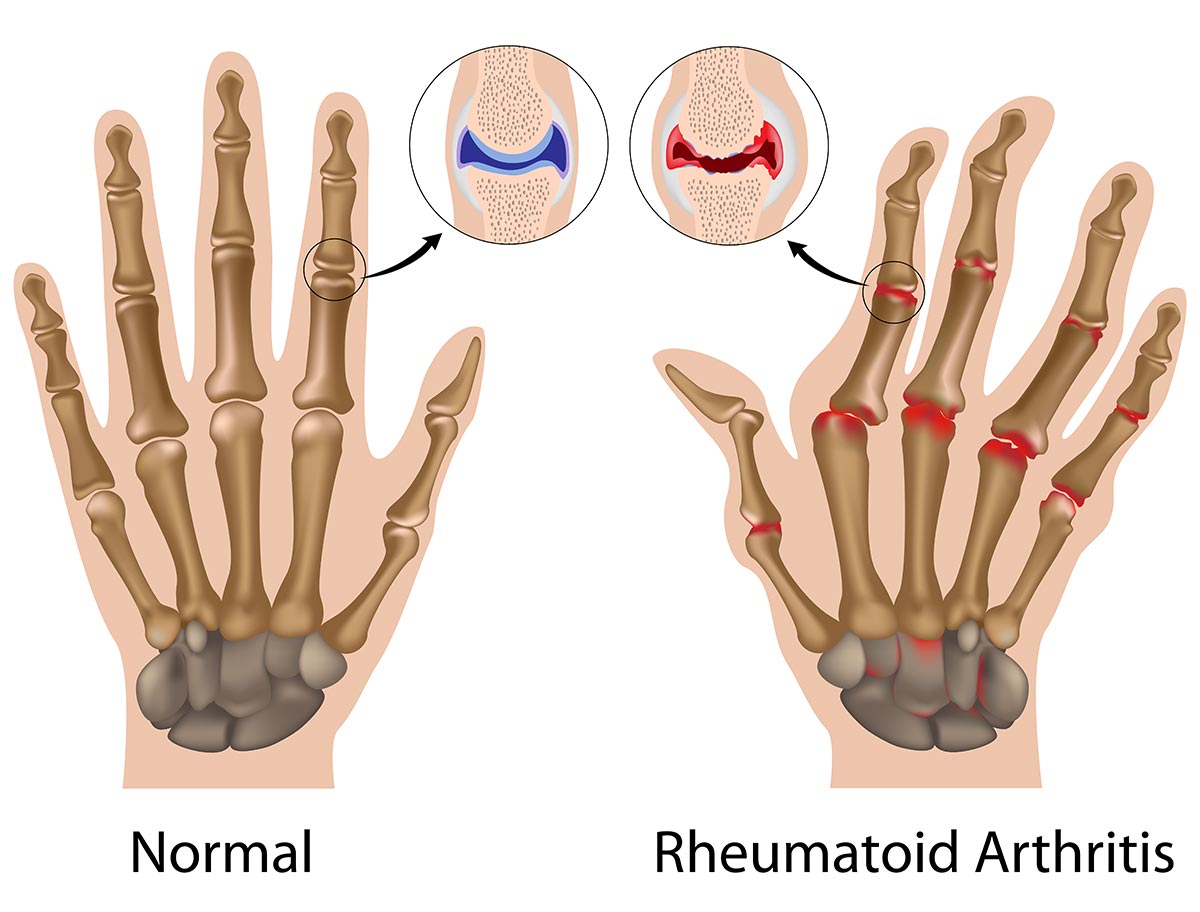
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disorder that impacts the joints in the body. Some patients experience severe damage in their body systems such as skin, eyes, lungs, heart and blood vessels. It is a chronic inflammatory disease that occurs when the immune system attacks the tissues in the body by mistake.
Rheumatoid arthritis is distinctive from osteoarthritis in a way that the lining of the joints is affected, it causes pain and swelling that may lead to bone erosion or joint deformity. Other parts in the body can also be impaired by inflammation that is rooted from rheumatoid arthritis. Innovative medications have been invented for significant improvements in treatment, but patients with severe stage of rheumatoid arthritis still have the chance to suffer from physical disabilities.
Symptoms
Rheumatoid arthritis may have the following symptoms and signs:
- Warm, swollen, tender joints
- Joint stiffness worse in the mornings and after long inactivity
- Stiffness and pain on both sides of your body in the same joints
- Fatigue, weakness, fever and decreased appetite
The initial stage of rheumatoid arthritis often starts with having an impact on joints that are smaller in size, especially joints between the hands and the fingers as well as the joints between the toes and the feet. Symptoms have the tendency to spread to the wrists, ankles, knees, elbows, shoulders and hips as the illness worsen.
However, to experience symptoms in other parts of the body aside from the joints is common in 40% of people. Seek medical advice if pain, discomfort, and swelling persist for a long time. Additional areas that may be affected in the body are skin, eyes, lungs, heart, kidneys, salivary glands, nerve tissue, bone marrow and blood vessels.
Causes
In a normal functioning body, immune system is supposed to protect the body from infections and diseases. When patients suffer from rheumatoid arthritis, the immune system is triggered by unidentified factor and attacks the healthy tissues that are located in the joints. This attack can have an impact on the heart, lungs, nerves, eyes and skin. A definite cause of this disease is unknown, however a genetic component seems to be a triggering factor. Human genes are not natural causes of rheumatoid arthritis but they can react to environmental factors such as infection that contains some viruses or bacteria that may cause the disease to develop.
Risk factors that may raise the chance developing of rheumatoid arthritis include:
- Gender: Females tend to develop rheumatoid arthritis more than males.
- Age: Patients of any age can develop rheumatoid arthritis, but generally it is more common to occur in middle age.
- Family history. If the patient has a record of a family member who has rheumatoid arthritis, the risk of developing the disease increases.
- Smoking. Smoking cigarettes raises the risk of obtaining rheumatoid arthritis, especially if the patient has a genetic predisposition of the disease. Smoking can also increase the severity of the disease.
- Overweight: Being overweight can accelerate the risks for rheumatoid arthritis to occur.























