Kidney cancer

Overview
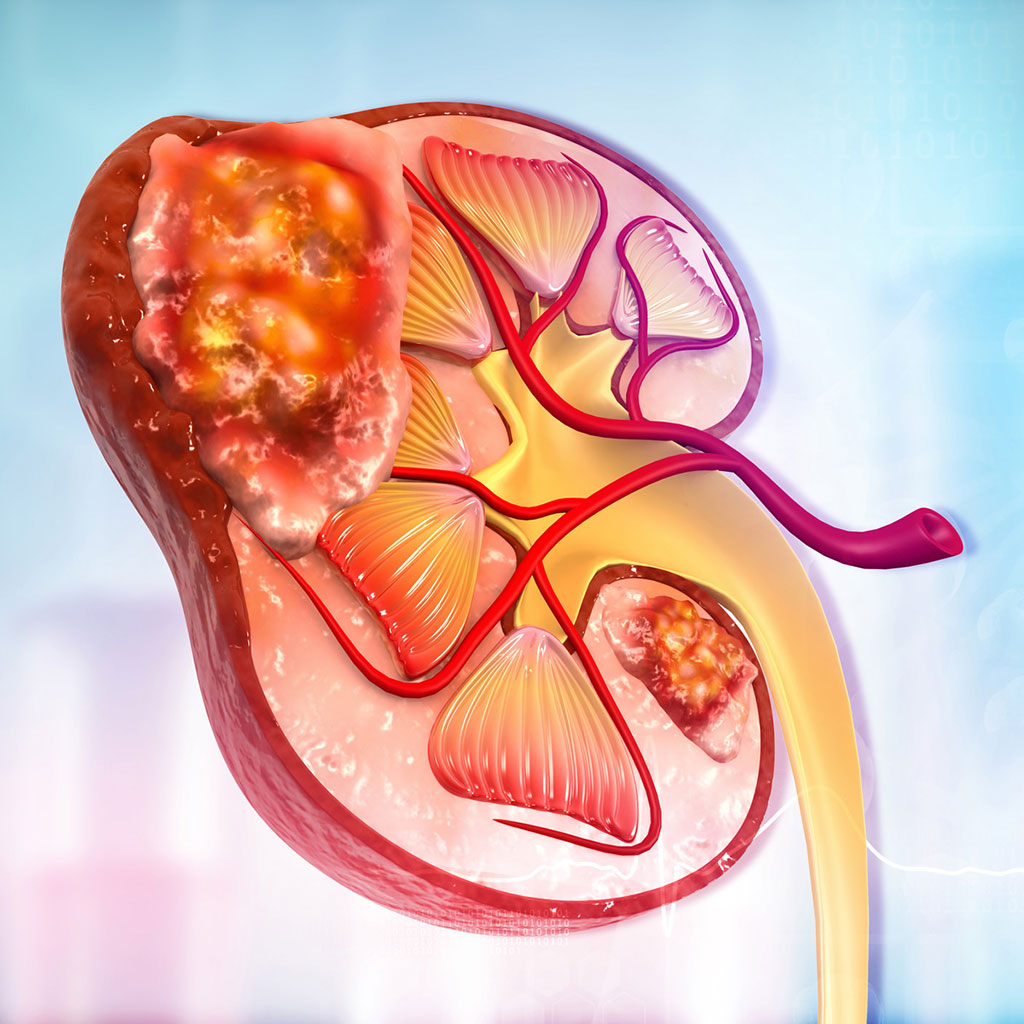
Kidney cancer also called renal cancer, is type of cancer that originate from the renal cell. Kidneys are two bean-shaped organs that is located below the rib cage, behind the abdominal organs.
The major function of the kidneys is to purify the blood, turn the waste products into urine, and control the body’s fluid balance. It also regulates blood pressure by producing renin (an enzyme that regulate and maintain blood pressure).
Early diagnosis of kidney cancer increases the chance for successful treatment. Treatment options for kidney cancers are surgery, cryoablation, radiofrequency ablation, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and radiation therapy.
Different types of kidney cancer
- Renal cell carcinoma (RCC): is the most common type of adult kidney cancer. It develops as a single tumor within one kidney, or sometimes both kidneys could be affected at the same time.
- Transitional cell carcinoma – the cancer can develop in the ureter or bladder. It begins at the transitional zone where the ureter connects to the kidney.
- Renal sarcoma – a rare type of kidney cancer that develops at the connective tissues of the kidney.
- Wilm’s tumor (nephroblastoma): is the most common kidney cancer in children.
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of kidney cancer are not likely to detected at an early stage. However, if there development of kidney cancer the signs and symptoms of are as follows:
- Hematuria (blood in the urine)
- Lower back pain
- Unexplained weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue / tiredness
- Low grade fever
- High blood pressure
If you notice any signs and symptoms that are persistent, make an appointment with your doctor. Investigation may be recommended due to that kidney cancer symptoms are not specific with cancer.
Causes
The cause of kidney cancer is unclear. Generally, cancer starts when the cell’s DNA mutates. This mutation causes the cells to grow and divide rapidly outliving the healthy cells, and later on forms a tumor which can invade surrounding tissue or spread to other part of the body.
Risk factors
Factors that may increase kidney cancer risk includes:
- Age: all age is at risk to develop kidney but higher risk as the person get older.
- Family history: it is highly possible to develop a kidney cancer if there is a history of cancer from the parents or siblings.
- Smoking: people who smokes have higher risk to develop kidney cancer compared to nonsmokers.
- Obesity: people who are obese have higher risk to develop kidney cancer.
- Hypertension (high blood pressure): people who have hypertension are at risk of kidney cancer.
- Dialysis: cleanse the blood by using a special machine, people who undergone a long-term treatment for kidney failure have higher risk to develop kidney cancer.
- Inherited syndromes: people who have inherited disorders such as Von Hippel-Lindau disease and Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome, and others have higher risk to develop kidney cancer.