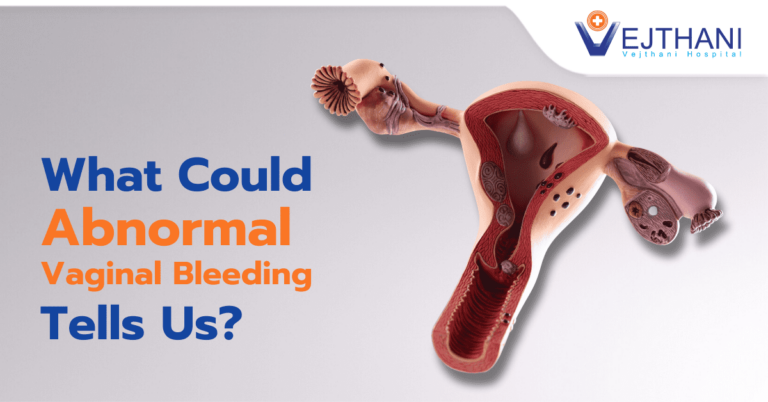
Ovarian cyst is one of the most common gynecologic condition found in out-patient clinic and gynecologic surgery.
An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac in an ovary or its surface.Women have two ovaries, each contains numerous eggs inside which are released in monthly cycles during childbearing years.
Most of the ovarian cysts are painless and harmless. They usually, disappear by themselves without treatment within a few months.However, if a cyst does not go away, gets bigger or causes any symptoms, it becomes a problem.
Symptoms of Ovarian Cyst
Women with a symptomatic ovarian cyst may have these symptoms:
- Pelvic pain: pain at the lower part of the abdomen, on the side where the cyst is
- Pain related to menstrual cycle
- Bloatedness, swelling or heaviness in the abdomen
- Palpable mass in the pelvic area
If the pain becomes a sudden sharp severe pain or pain with fever and vomiting, it may be an indication of a complication from an ovarian cyst. The patient will be suggested to undergo a medical investigation immediately.
Cause of ovarian cyst
There are several types of ovarian cysts. The most common types include:
- Functional Cyst: Cysts caused by a normal monthly function of the ovary. These cysts are usually harmless, rarely cause pain and often disappear within 2-3 menstrual cycles.
- Dermoid Cyst: Cyst caused by abnormal development of the embryonic cell. It may contain fat, hair or bone content.
- Endometrioma: Cyst caused by endometriosis, also called a chocolate cyst. The patient usually has a painful menstruation.
- Cystadenoma: Cyst develops on the surface of the ovary and may contain watery or mucous fluid.
Treatment of an Ovarian Cyst
Treatment depends on the patient’s condition, age, symptom and characteristic of the cyst.
- Wait and follow up. In simple, small, watery cyst with no symptom, the doctor may recommend patients to wait and follow-up by pelvic ultrasound. If there are changes in size, characteristics of the cyst or patient’s symptom, further investigation and treatment will be considered.
- Medication. Some hormone-related ovarian cyst may be decreased in size with hormone-medication treatment such as oral contraceptive pills. The doctor may prescribe birth control pills for a few months and monitor the ovarian cyst.
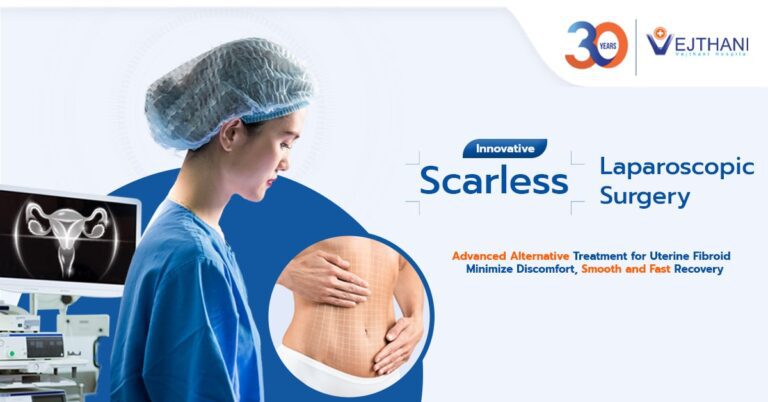
- Surgery. Surgical treatment might be recommended in a growing, large, complicated cyst. Cyst with complication or not responsive to medical treatment is recommended to be removed by surgery.Surgical treatment includes removing the cyst (cystectomy) or removing the entire affected ovary (oophorectomy).According to a worldwide standard, ovarian cyst that is not suspected as cancer should be removed by surgery through laparoscopy. This technique can perform both cystectomy and oophorectomy.The advantages of this technique are less pain, small surgical scar, short duration of hospitalization and faster recovery period compared to laparotomy (open surgery).
- Readers Rating
- Rated 4 stars
4 / 5 ( Reviewers) - Excellent
- Your Rating