According to World Health Organization (WHO), 10% or 5.5 million of deaths worldwide is caused by Stroke. So far, it is one of the highest percentages among the leading diseases in the world. There are two types of stroke – Ischemic Stroke and Hemorrhagic Stroke.
Ischemic strokes are the most common and arise from blood vessel narrowing caused by cholesterol as with CAD, leading to blood clot formation and cause brain infarction.
Hemorrhagic strokes are more common in some populations, who have high blood pressure especially in Asia and it results from the rupture of a blood vessel or aneurysm. The outlook is usually bleak with a mortality rate as high as 50% and some of these patients were left with disabilities. Both types of stroke can strike for a multitude of reasons.
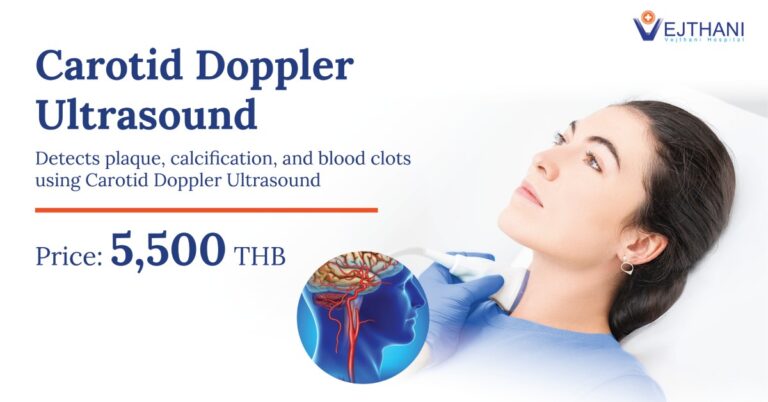
Today, people would mostly go with prevention other than cure. Bad lifestyle is one of the most common causes of stroke. For those who are health conscious and who already had a family member having stroke, a healthy lifestyle should be followed and regular checkups would be a good choice. There are also some of diagnostic procedures which can determine the chances of having stroke and one of them is Carotid Doppler Scan. A carotid artery stroke is preventable and can be treated better in early stage as possible.
The carotid arteries are located along both sides of the neck. They supply blood directly to the brain. Blocked carotid arteries are major risk factors for a carotid artery stroke.
WHAT are the blockages in carotid arteries that cause strokes to strike?
As we grow older, our arteries are becoming stiff with platelet and cholesterol, sticky substances called deposit or plaque. When plaque builds up in the carotid arteries, it is called carotid artery stenosis and this can result in a carotid artery stroke. Plaque buildup can pose the following risks to individuals:
- Smoking
- Lack of exercise
- Poor diet high in fat and cholesterol
- Being overweight or obese
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Genetic problems
WHAT IS CAROTID DOPPLER SCAN?
Carotid doppler is an ultrasound test that shows how well blood is flowing through the carotid arteries which is done in a vascular laboratory or radiology department. It is a painless method that uses sound waves to create images of the arteries and the flow that is going through. The scan is done if a doctor suspects that a stroke might strike.
Carotid doppler scan may also be called carotid artery duplex scan, carotid ultrasound, vascular ultrasound, and carotid artery Doppler sonography. It combines two types of ultrasound (sound waves) as follows:
Conventional Ultrasound
Also called B-mode, uses sound waves that bounce off blood vessels to provide a picture of your blood vessel structure.
Doppler ultrasound
This type of ultrasound uses sound waves that views blood moving through the vessel. The doctor can see how the blood is moving through wave form or velocities. Patients undergoing the carotid duplex scan may feel some pressure as the transducer is moved around the neck. The pressure should not cause any pain. The patient may also hear a “rushing” sound during the procedure.
WHY PERFORM CAROTID DOPPLER?
Carotid artery and its branches are the major areas of stroke. The rough plaque buildup in the carotid arteries can be detected by Carotid Duplex and a carotid artery stroke can be prevented as early detection indicated.
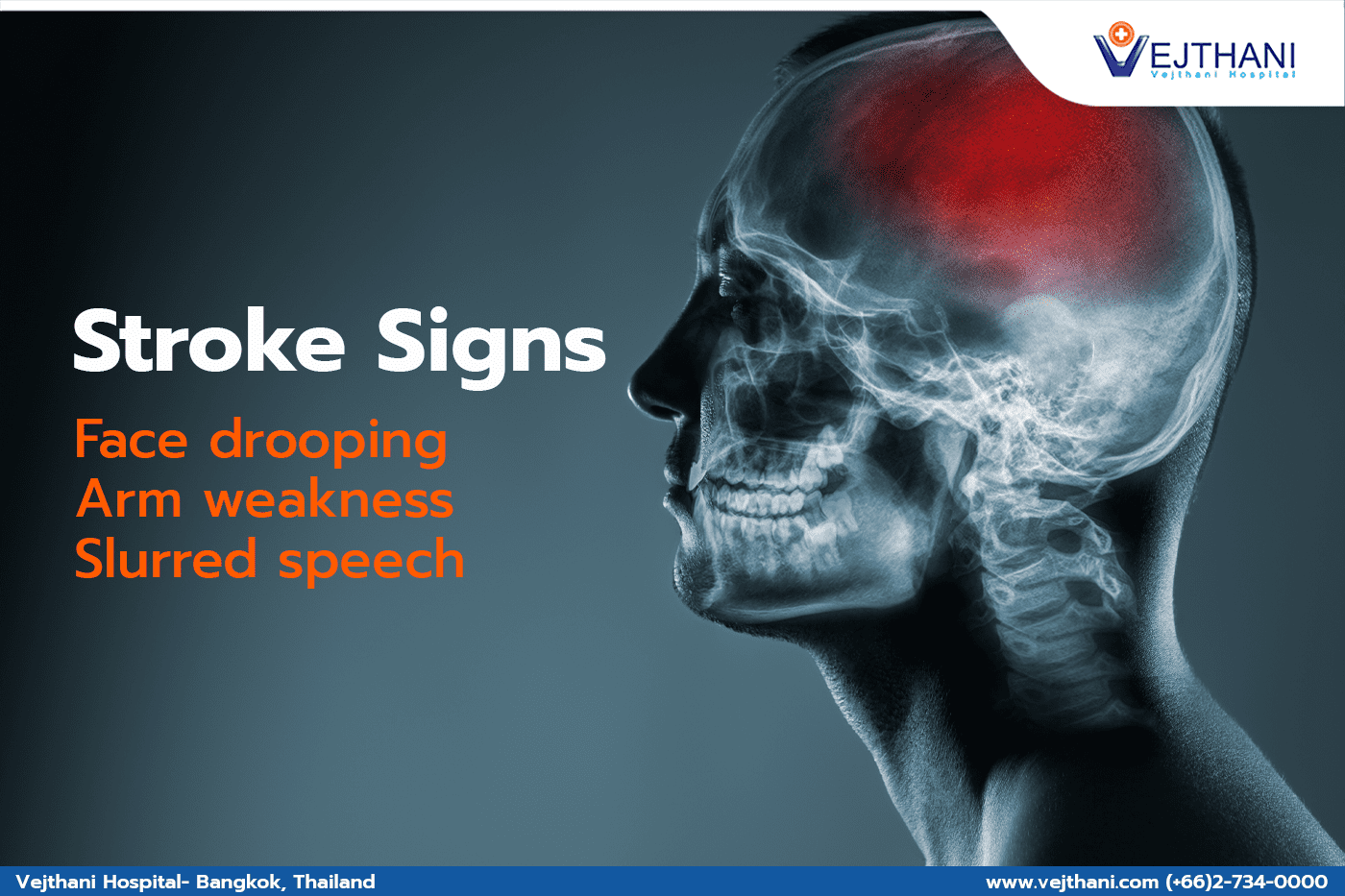
Some early warning signs of carotid artery disease which is typically a warning sign of stroke or mini-stroke can include:
- Weakness, numbness, or tingling on one side of the body or in your arm or leg
- Inability to move your arm or leg
- Inability to speak clearly
- Inability to see in one eye
If you experience any of these warning signs, even if they go away, it’s important that you see a doctor immediately. It could mean that you have had a stroke or a stroke might strike soon.
The doctor will ask you questions about your symptoms and your medical history. He/she may also listen to the blood flow in your neck and will measure your blood pressure. If the doctor thinks you have carotid artery disease, he or she will order a carotid duplex. Scan first, then may pursue with MRI scan of the brain, the artery (MRA) or the vein (MRV).
WHAT CONDITIONS CAN BE DETECTED BY DUPLEX SCAN, MRI, MRI, OR MRV?
- Blood clotting (thrombosis)
- Narrowing in the arteries (stenosis)
- Other causes of blockage in the carotid arteries
- Bleeding in the brain or intracranially
The doctor can provide treatment immediately thereafter.
ADVANTAGES OF CAROTID DOPPLER SCAN
- No preparation is necessary. The test is non-invasive.
- There are no risk with having this procedure and no pain.
- Can detect pending stroke attack by viewing arterial diseases.
FACTORS WHICH MAY INTERFERE WITH RESULT
- Severe obesity
- Irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias)
- Cardiac disease
- Inexperienced Technicians
Normal Results
The images and the flow patterns will determine the conditions of the arteries. For example, the arteries may be 10% narrowed, 50% narrowed, or 75% narrowed. A normal result means there is no problem with the blood flow in the carotid arteries or the images of the arterial wall and the likelihood for a stroke to strike is reduced.
What Abnormal Results Mean
An abnormal result means the artery may contain plaques at the wall of the carotid arteries, which means a carotid artery stroke is possible. This is a sign of atherosclerosis in which the stenosis can be determined along with the flow pattern. Some severe narrowing may be asymptomatic and stenosis is more than 70%, then physician may obtain more imaging to:
- Consider surgery
- Have additional tests (such as cerebral angiography, CT angiography, and magnetic resonance angiography)
- Follow a healthy diet and lifestyle to prevent hardening of the arteries
- Repeat the test again in the future
Preparation
- The doctor will explain the procedure and offer the opportunity to ask any questions about the procedure.
- A consent form may be asked to sign that you are giving permission to do the procedure. Read the form carefully and ask questions if something is not clear.
- The doctor may give specific instructions about smoking and consuming caffeine. You may be asked to refrain from smoking for at least 2 hours before the test, as smoking causes blood vessels to constrict. You may also be asked to refrain from consuming caffeine in any form for about 2 hours prior to the test.
- Based on your medical condition, your doctor may request other specific preparation.
During the Procedure
It may be performed on an outpatient basis or as part of your stay in a hospital. Procedures may vary depending on your condition and your doctor’s practices.
Generally, a carotid doppler scan follows this process:
- You will be asked to remove any clothing, jewelry, or other objects that may interfere with the scan from your neck.
- If you are asked to remove clothing, you will be given a gown to wear.
- You will lie on an examination table with your neck slightly extended (bent backward).
- A clear gel will be placed on the skin at various locations on the carotid arteries.
- The Doppler transducer will be pressed against the skin and moved around over the area of the artery being studied.
- When blood flow is detected, you will hear a “whoosh, whoosh” sound. The probe will be moved around to compare blood flow in different areas of the artery. Both sides of the neck will be examined.
- Once the procedure has been completed, the gel will be wiped off.
The technologist will use all possible comfort measures and complete the procedure as quickly as possible to minimize any discomfort.
After the Procedure
While the carotid artery duplex scan procedure itself causes no pain, having to lie still for the length of the procedure might cause slight discomfort.
There is no special type of care required after a carotid doppler scan. You may resume your usual diet and activities unless the doctor advises you differently.
There may be other reasons for your doctor to recommend a carotid Doppler scan to be repeated at certain period of time to prevent any carotid artery strokes in the future.
Vejthani Hospital Neuroscience Center’s Neurology Department is a medical specialty department dealing with disorders of the nervous system. Specifically, it deals with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of disease involving the central, peripheral, and autonomic nervous systems such as headache, muscle weakness, carotid artery stroke, convulsion, head injury, or infection of the Central Nervous System.
Vejthani Neuroscience Centeris an integrated center of Neurological Services. This center has many experienced and qualified neurologists and neurosurgeons in different subspecialties joining forces with other paramedical and neurological nurses, technical teams and rehabilitation team. Vejthani neuroscience center offers competent out-patient and in-patient services.
Patients can be assured of receiving an excellent international level of care for both selective and emergency needs.
For more information, please contact
Neuroscience Center, Vejthani Hospital
Call: (+66)2-734-0000 Ext. 5400
English Hotline: (+66)85-223-8888
- Readers Rating
- Rated 5 stars
5 / 5 ( Reviewers) - Spectacular
- Your Rating