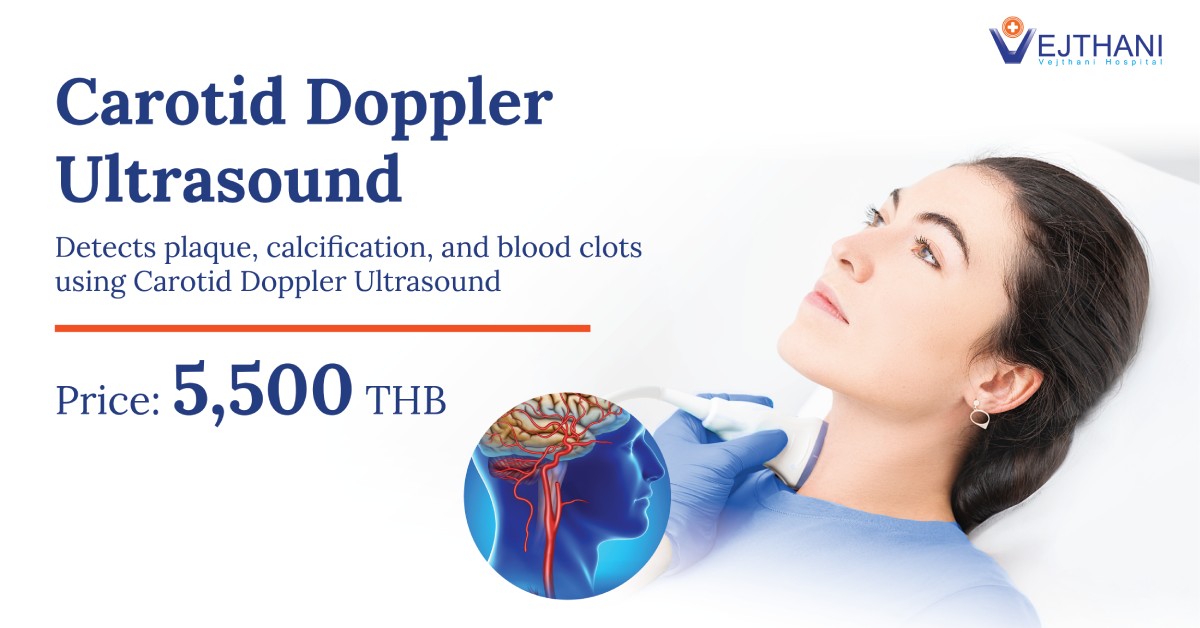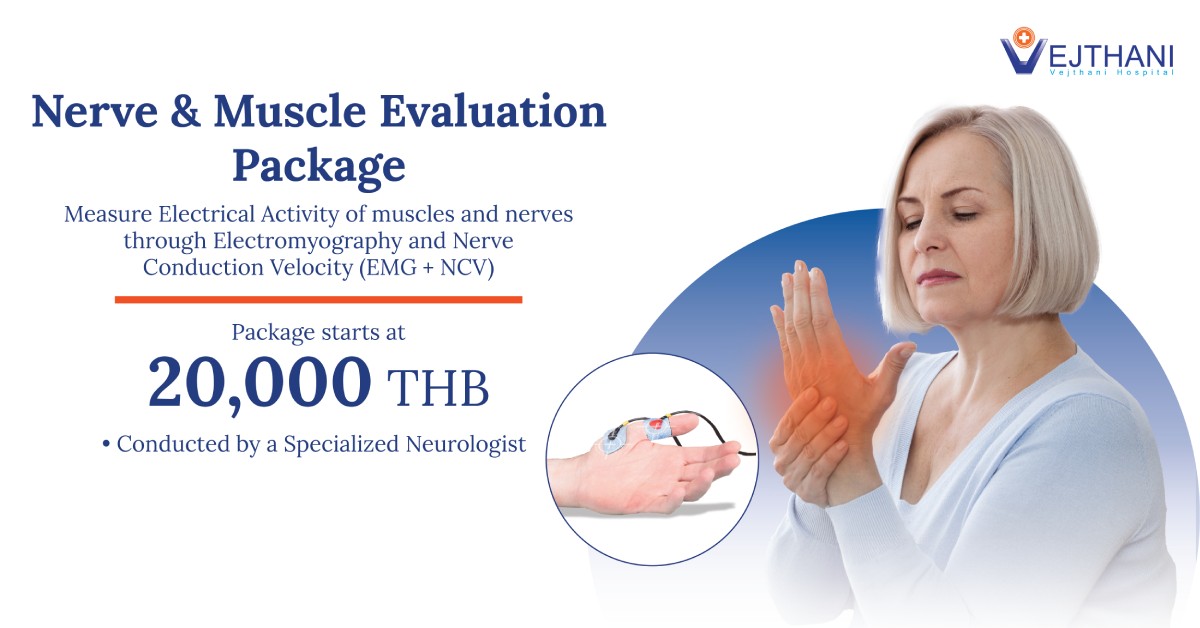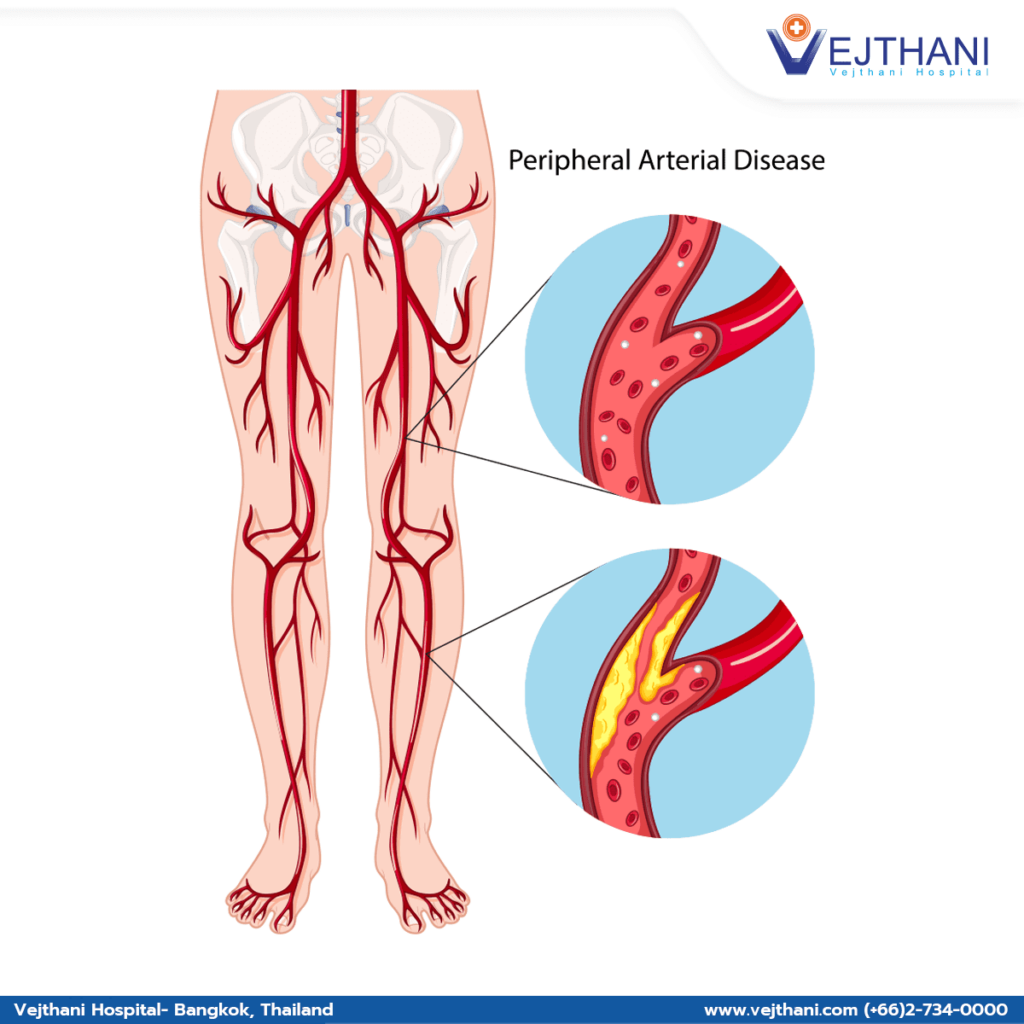

Peripheral artery disease is a common disease that involves the narrowing of arteries, causing diminished blood circulation to the arms or legs. The arms or usually the legs, receive inadequate blood supply, which can lead to leg pain and other symptoms when walking.
Peripheral artery disease indicates the buildup of fatty deposits within the arteries known as atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis leads to the constriction of arteries, which in turn can decrease blood circulation in the legs and occasionally the arms.
Treating peripheral artery disease involves engaging in physical activities, consume a nutritious diet, and refraining from smoking or tobacco use.
Peripheral artery disease in numerous people shows subtle or no symptoms at all. In some cases, people experience pain in their legs while walking, a condition known as claudication.
Claudication symptoms such as muscle aches or cramping in the arms or legs, initiated by exercises and alleviated by resting. The pain predominantly occurs in the calf region and varies in intensity from mild to severe. Severe leg pain, mobility or engagement in various physical activities might become challenging.
Other symptoms of peripheral artery disease may include:
- Feeling cold in lower leg or foot, when compared to the other side
- Numbness or weakness in the legs
- Absent or weak pulse in the legs or feet
- Painful cramps in the hips, thighs, or calf muscles following certain activities like walking or climbing the stairs
- Skin on the legs appearing glossy
- Changes in skin color on the legs
- Delayed toenail growth
- Persistent non-healing sores on the feet, toes, or legs
- Pain, ache and cramps when using the arms such as knitting, writing, or performing manual tasks
- Erectile function
- Hair loss or decreased hair growth on the legs
Top of Form
As peripheral artery disease progresses, pain might arise even when resting or reclining. This pain could disrupt sleep and can be temporarily alleviated by hanging the legs off the edge of the bed or when walking.
In rare cases, inflammation of blood vessels or arms/ legs injury or changes in the muscle ligaments or expose to radiation could cause peripheral artery disease.
Smoking or having diabetes significantly enhances the likelihood of developing peripheral artery disease. Additionally, a family history, heart disease or stroke, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, high levels of homocysteine, which increase the risk for coronary artery disease, aging especially after 65 or obesity could elevate the risk as well.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle could prevent the symptoms caused by the disease. A healthy lifestyle includes no smoke, control blood sugar, and consume food that have low saturated fat. Exercise regularly by consulting with your doctor for the right physical activity, maintain a healthy body weight and manage blood pressure and cholesterol.
Apart from medications to control the symptoms peripheral artery disease could be treated by
- Angioplasty and stent placement is done to unclog the constricted arteries. . It serves a dual purpose of diagnosing and treating blocked vessel by inserting a catheter to navigate to the constricted section of the artery. A small balloon inflated, so the blocked artery is widened, promoting enhanced blood circulation. In some cases, a minute wire mesh tube (stent) could be positioned within the artery to keep it open.
- Bypass surgery is done by creating an alternate route around the obstructed artery, through either a healthy blood vessel from another region of the body or an artificial substitute.
- Thrombolytic therapy is preferred when an artery is obstructed by a blood clot, medication designed to dissolve clots can help treat the affected artery.
Early detection and intervention play a crucial role in managing peripheral artery disease and reducing the risk of complications. If left untreated, PAD can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life and increase the likelihood of severe cardiovascular events. Therefore, seeking medical attention at the first sign of symptoms is paramount.
- Readers Rating
- Rated 5 stars
5 / 5 ( Reviewers) - Spectacular
- Your Rating