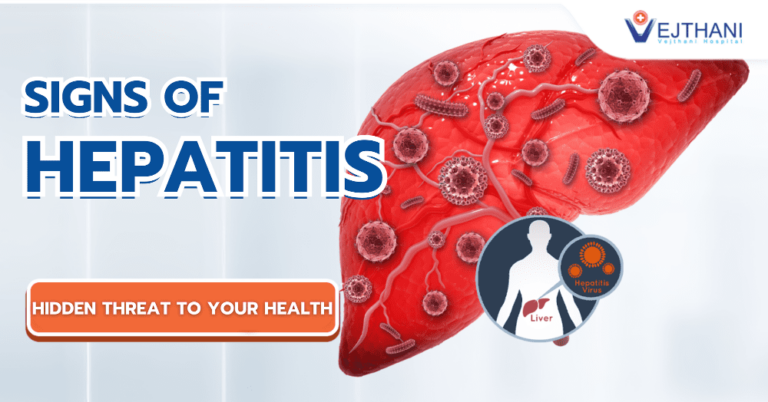

There are 5 kinds of Hepatitis viruses, which include hepatitis virus A, B, C, D and E, with most common viruses being hepatitis virus B and C and less common are hepatitis virus D and E. There are 2 types of common symptoms among persons with hepatitis virus including:
Acute infections
Patients will develop fever, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, rash and joint pain. Afterwards, fever will be reduced and the patient will have yellow eyes and yellow body.
Chronic infections
Patients often have no symptoms, or have non-specific symptoms such as fatigue and slight weakness. There might be complications in patients infected for a long period of time such as cirrhosis and liver cancer, which may be found in the later stages of the disease. A blood test can reveal the pathogens that cause chronic hepatitis which include hepatitis virus B, C and D.
Hepatitis A virus
Hepatitis virus A is contacted by consuming food or water that is contaminated with the virus with an incubation period of 2-6 weeks. Infection in most children occurs with little or no symptoms. However, adults will develop symptoms of acute hepatitis that are more severe and clear, which include yellow eyes, yellow body, fatigue, nausea and vomiting. Patients infected with hepatitis A do not develop chronic hepatitis.
Hepatitis B virus
Hepatitis B virus is a major cause of chronic hepatitis including cirrhosis and liver cancer. Data from the Hepatitis Foundation reveal that 350-400 million people are infected with hepatitis B virus. Although today there is a vaccine against hepatitis B, Thailand still has high outbreaks of the hepatitis B virus.
Transmission of Hepatitis B virus
Not from food, saliva or touch but through 3 ways which are Blood or blood components such as injection into the veins, tattoos, ear piercing or combined use of sharp objects.
Infections from mother to child Sexual intercourse Treatment
Patients with the acute phase maybe admitted to the hospital to watch out for acute liver failure but in cases of chronic hepatitis or with carriers of the disease, medication is administered in the form of injections or oral medications which can reduce the amount of virus and inflammation of the liver, thus reducing the chances of cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Hepatitis C virus
Hepatitis C virus is another important cause of cirrhosis and liver cancer and can be transmitted the same way as hepatitis B virus. There are more than 100 million people infected with hepatitis C virus today with data from blood donations in Thailand revealing that 1-2% of the population found to be infected with the virus. To date, there is still no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C virus. Patients with hepatitis C virus do not have any abnormal symptoms and the virus can only be found through a blood test with 50-90% developing chronic hepatitis C. If hepatitis C is left untreated, it is bound to develop complications such as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Treatment
Hepatitis C virus is treated through injections once a week and daily medication for 24-48 weeks depending on the species of the bacteria which constitute 6 types in total. Hepatitis C is more easily curable than hepatitis B therefore; patients infected with hepatitis C should seek prompt medical attention.
Recommendations for the patients with Hepatitis
- Avoid drinking alcohol and smoking.
- Avoid taking drugs unnecessarily. Ask your doctor which drugs affect the liver.
- Avoid the use of herbal supplements
- Rest well
- Avoid vigorous exercises
- Have regular checkups to watch out for cirrhosis and liver cancer
- Advise to close relatives, siblings, husbands and wives to check for the virus and to be vaccinated for protection
- Be careful of transmitting the virus to others
- In the case of treatment required, continuity must be necessary to achieve progress
- Males more likely to contract Hepatitis
During the end of 2011, the Liver Disease Foundation organized the 8th “We Love Liver” campaign for the general public to administer free liver enzyme (ALT) checkups with 69 private hospitals participating across the country. 7,733 people were tested in total, with 904 or 11.69% of people having abnormal results. It was found that men had 2.58 times more abnormal results than women with abnormal results in 19.30% of males and 7.49% in females. Vejthani hospital had 113 test participants, including 37 males and 76 females with total 12 abnormal results, including 9 males and 3 females. These results show conclusively that males are 3 times more likely to have hepatitis than females.
Hepatitis is a public health issue that most people are not sufficiently aware of the risks with patients coming for treatment to the doctor at the later stages of the disease resulting in a lot of deaths due to cirrhosis and liver cancer. Therefore, if you have not been infected you should be vaccinated for immunity while those who have been infected should have regular check ups to monitor the progression of the disease.
For more information, please contact
Gastroenterology and Hepatology Center,
2nd floor, Vejthani Hospital
Tel.: 02-734-0000 ext 2960,2961,2966
- Readers Rating
- Rated 5 stars
5 / 5 ( Reviewers) - Spectacular
- Your Rating