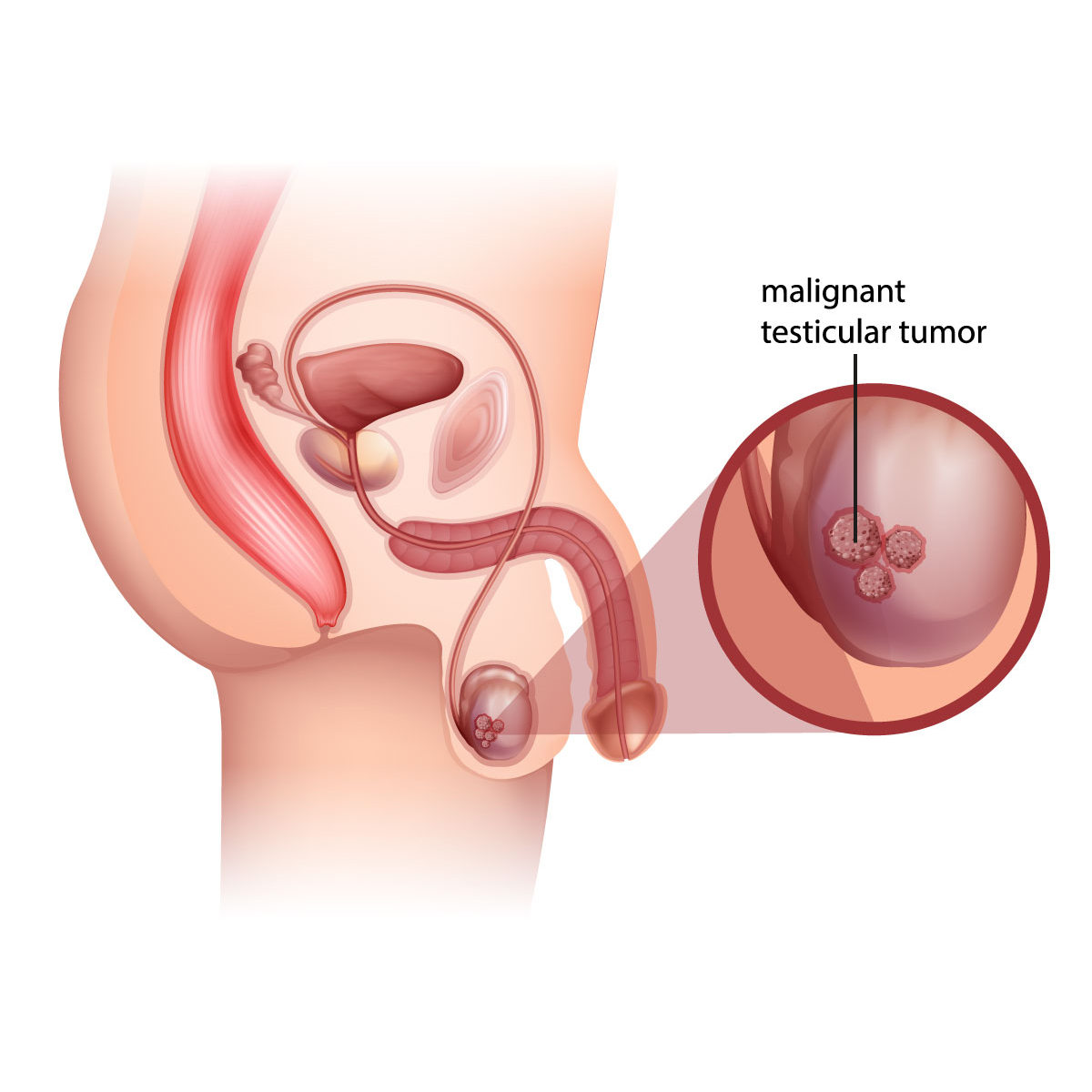
Overview
Testicular cancer is the development of cancer cell at either one or both testicles. Testicles are the two walnut-shaped glands that is located inside the scrotum (sac of skin under the penis), which produce male sex hormone and sperm. Testicular cancer is highly treatable even if the cancer has spread. Treatment for testicular cancer is based on the type and stage of the cancer.
Different types of testicular cancer
Most testicular cancers start in cells known as germ cells. These are the cells that develop into sperm.
There are two types of germs cells:
- Seminoma: These are more commonly in those that are of older age and tend to grow slower than non-seminoma.
- Non-seminoma. These grow rapidly and usually affect people in the late teen and early 30’s and are known to spread rapidly. The four types of non-seminoma tumors are named after its type of germ cell that they originate from. Non-seminoma tumors include embryonal carcinoma, yolk sac carcinoma, choriocarcinoma and teratoma.
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of testicular cancer are as follows:
- Painless lump in the testicles
- Enlargement or swelling at either side of the testicles.
- Pain or discomfort at either the testicle or the scrotum
- Dull ache at the groin or abdomen
- Swelling or feeling of heaviness in the scrotum
If you notice any signs and symptoms that are persistent for more than two weeks, then you should make an appointment with your doctor.
Causes
In most cases the cause of testicular cancer is unknown how it could be from the multiplication of cancer cell that eventually developed into a tumor or a lump. The most common testicular cancer usually starts with the germ cells that formed into a tumor.
Risk factors
Factors that may increase testicular cancer risk includes:
- Age: it usually affects the late teens or men at early 30’s, however it could still affect male at all ages.
- Family History: it is highly possible to develop a testicular cancer if there is a history of cancer from the biological father or siblings.
- Undescended testicle: being born with undescended testicles (testicles fails to move from the abdomen to the scrotum before the birth) may increase the risk of having testicular cancer even it was surgically corrected.
- Race and ethnicity: testicular cancer are more common among white men.
Diagnosis
It is highly recommended for men to perform testicular self-examination (TSE) to check for lumps. The lumps could also be detected during the routine physical examination with the specialist.
To properly diagnose the testicular cancer, the following procedures may be recommended:
- Ultrasound: A painless procedure that uses sound waves to create an image of both the scrotum and the testicles. Ultrasound imaging also can used to locate and evaluate tumor (solid or fluid-filled) in the testicle or the scrotum.
- Computerized tomography (CT) scan: Uses X-ray images of the abdomen, chest, and pelvis to determine the extent of the cancer.
- Blood tests: to determine the amount level of substances that is linked to a specific cancer type, this substance is called tumor markers. High level of tumor markers at the blood could not possibly indicate cancer; however, the test could help determine the diagnosis.
- Inguinal orchiectomy and biopsy. If the lump at the testicle could be cancerous, then surgical procedure to remove the testicle is recommended, and the sample will be sent to the laboratory to evaluate for any sign of cancer. The biopsy result will also help determine the cell type involved.
Staging
Once the specialist confirmed the diagnosis of the testicular cancer, the following step is to know the extent (stage) of the cancer. The stages of cancer are indicated by Roman numerals ranging from 0 to III. The lowest stage indicates a cancer is confined at the limited area around the testicle. The highest stage – stage III – indicates that the cancer had spread and advanced in other areas of the body.
Treatment
The type, location and stage of cancer are some of the factors which can affect the type of treatment to apply as well as general health and personal choice of treatment. The treatment options are as follows:
Surgery
Surgery could be recommended to remove the affected testicle considering the size, location, and stage of the testicular cancer.
- Radical inguinal orchiectomy: This is the surgical procedure to remove the affected testicle. This is used for both seminoma and non-seminoma testicular cancer. During the procedure, an incision will be made at the groin area to remove the testicles with the tumor. This can be the only treatment needed for early stage of testicular cancer.
- Retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (RPLND): This is the surgical removal of the abdominal lymph nodes to treat testicular cancer and may also be used for cancer staging. During the procedure, an incision will be made at your abdomen and removes the lymph nodes behind the abdominal organs.
The doctor might monitor closely after surgery. The appointment may include blood test, CT scan and other procedures to check for early sign of the cancer relapsing.
Chemotherapy
The use of specific drugs to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy enters the bloodstream and travels throughout the body. The chemotherapy could be done either before or after the removal of the lymph nodes. Infertility is a common side effect during chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Radiation therapy
Tumors are eliminated by radiation therapy using high-energy radiation. Radiation therapy is an option that can be combined with chemotherapy when surgery cannot be done to totally remove the cancer cells. This treatment is recommended for seminoma type of testicular cancer.




