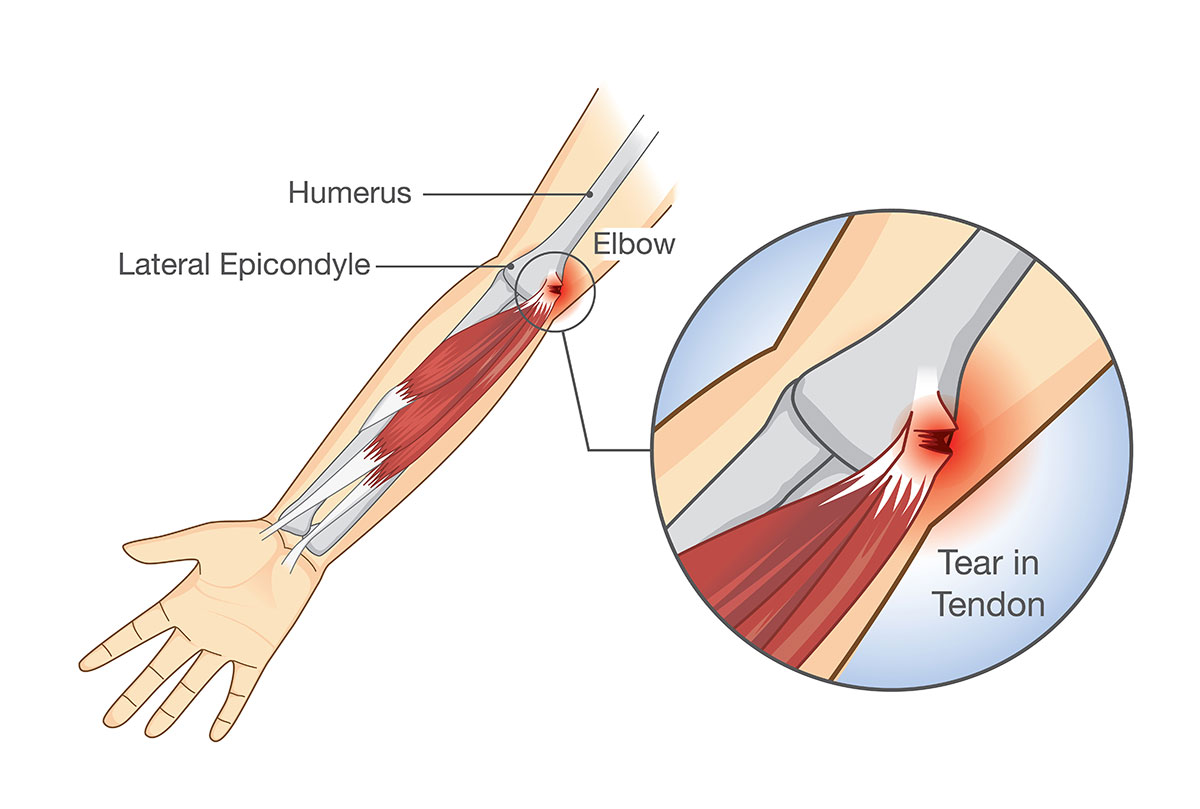
Overview
Golfer’s elbow, also known as Medial epicondylitis or Medial elbow tendinopathy, is a condition caused by generation change of the tendon that connects your forearm muscle to the bone at the inner elbow. Usually, this tendon controls the movement of the wrist and fingers flexion.
Athletes such as golfers or tennis players who often utilize their wrist to grasp their gears tightly are also prone to golfer’s elbow. This is the reason why it is almost comparable to tennis elbow. The only difference is that, tennis elbow occurs on the outer side of the elbow. Moreover, the pain can sometimes extend to the forearm and wrist.
Symptoms
The following are symptoms of golfer’s elbow:
- Tenderness and pain on the inner area of the elbow, and may extend to the inner forearm.
- Stiffness on the elbow may be felt when you make a fist.
- Weakness of the hand and wrist.
- Numbness or tingling sensation on either the ring or little finger, or both.
When to see a doctor:
- Persistent elbow pain
- Inflammation of the elbow
- Limited your activities of daily living
- Elbow deformity
- If fractured elbow is suspected
Causes:
Repetitive or overuse of the wrist and fingers by faulty movements may lead to a small injury to the tendon which causes golfer’s elbow.
Other activities or job that may cause golfer’s elbow are:
- Throwing sports: Faulty technique or movement during sports which involves throwing (e.g. archery, football or javelin) or pitching (e.g. baseball or softball).
- Weight training: Faulty techniques when carrying heavy weights.
- Jobs that require repetitive heavy force on the elbow, forearm and wrist area: For example office workers who are pounding on keyboards when typing, waiters lifting heavy food trays, carpenters, plumbers or construction workers.
People aged 40 and above, obese, smoker and performs repetitive tasks using their arms are at risk of developing golfer’s elbow.
Diagnosis:
Doctor will evaluate the medical history and perform a physical examination. These include performing movement of the joint and applying pressure to the joint which could result in pain or stiffness.
To find out other abnormalities such as arthritis, broken bones or nerve compression, the following tests may be requested:
- X-ray
- Ultrasound / Computed Tomography (CT) scan / Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Electromyography (EMG)
Treatment:
- Rest: Promotes healing and prevents elbow from weight-bearing and overuse activities for at least six weeks.
- Ice: Apply ice for 20 minutes every 2 hours while awake to prevent or minimize swelling.
- Elevation: Elevate your elbow on a pillow while lying down.
- Stretching and strengthening: Specific exercises to stretch and strengthen the muscles that attach to the site of the injured tendon after pain subsides, this will help with the healing process.
- Using golfer’s elbow brace: Doctor might recommend you to use a counterforce brace to reduce tendon and muscle stress.
- Over-the-counter pain reliever: Medications such as ibuprofen, naproxen sodium or acetaminophen can be taken.
- Injection of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): This technique collects a few amounts of your blood. The platelets and other anti-inflammatory factors from the blood will be injected back to the affected area.
- Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT), Laser therapy
Surgery
Surgery is not usually indicated to treat Golfer’s elbow unless non-operative treatments have failed to improve the range of motion and decrease pain. Doctor may recommend surgery to remove the damaged tissue and repair the tendon. After the surgery, you must undergo physical therapy for recovery. If left untreated a golfer’s elbow can lead to long-term elbow pain and permanent grip weakness. If your pain is relieved, you may continue regular activities again.