Carotid Artery Treatment
Overview
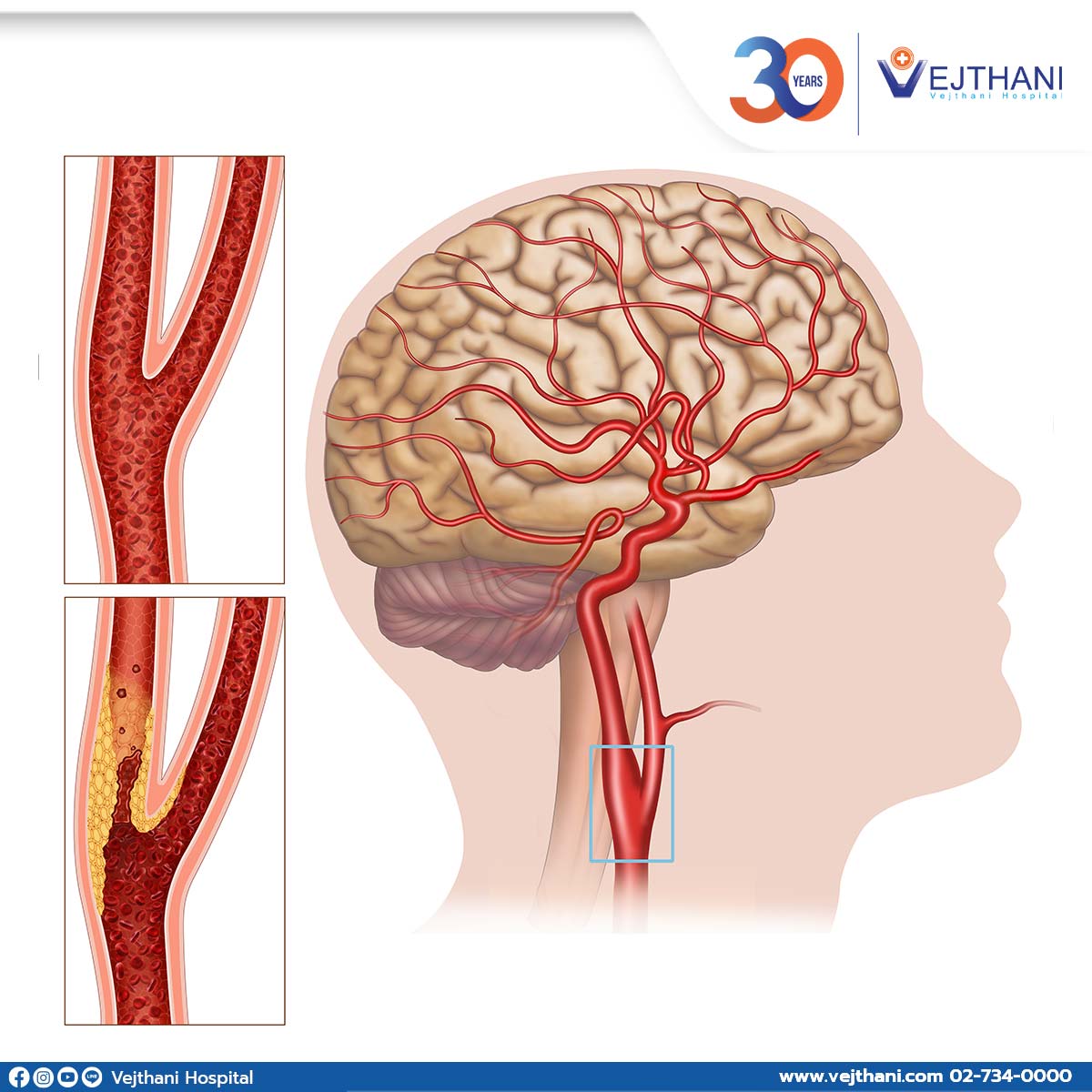
Carotid artery disease is caused by plaques (fat deposits) that block the blood vessels (carotid arteries) which carry blood to the brain and head. This disease takes time to develop.
The onset of the disease can come from the interference of the blood supply to the brain, which leads to transient ischemic attack (TIA). TIA happens when there is less blood delivered to the brain, which occurs temporarily and causes a stroke. Stroke leads to dead brain cells as the brain loses oxygenation.
Changing your lifestyle, taking medications, and undergoing surgery are some of the treatments for carotid artery disease.
Symptoms
There are usually no symptoms when carotid artery disease is just starting, and the disease tends to be overlooked until stroke or TIA suddenly occurs.
The following are the signs and symptoms of a TIA or stroke:
- Numbness or weakness, often on one side of the body
- Sudden severe headache that occurs without any reason
- Slurred speech and a problem with understanding
- Eyesight problem on one or both eyes
- Dizziness or suddenly feeling out of balance
Call for emergency medical help if you suddenly experience symptoms of a stroke. A doctor must be consulted immediately because it may be a TIA or a sign of an impending complete stroke.
If you have the risk factors to develop a carotid artery disease, consult your doctor to be able to receive suggestions on how to control your risk factors. Early detection increases the chance of treatment before the debilitating effects of stroke occur.
Causes
The accumulation of plaques in the arteries that brings blood up to your brain causes carotid artery disease requiring treatment. Plaques are formed from cholesterol, fibrous tissue, calcium, and other cell particles that are deposited on small injury sites inside the artery. This leads to atherosclerosis. Arteries become hard and narrow due to the buildup of plaques. This inhibits the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the brain.
Risk factors
These are the risk factors that may lead to carotid artery disease:
- High blood pressure: When the arterial walls experience extreme pressure, they become prone to injury.
- Diabetes: Diabetes decreases fat processing ability, which holds a higher risk of developing high blood pressure and atherosclerosis.
- High blood-fat levels: When low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and triglycerides (blood fat) levels increase, the buildup of plaques will be increased.
- Age: Aging causes the arteries to be stiff and at risk for injury.
- Family history: Having a family member with coronary artery disease or atherosclerosis increases your chance of developing a carotid artery disease
- Lack of exercise: Being inactive leads to obesity, diabetes and high blood pressure.
- Obesity: Being overweight puts you at risk of having atherosclerosis, high blood pressure and diabetes.
- Tobacco smoking: The artery walls are irritated from the nicotine, which also causes high blood pressure and increases heart rate.
- Sleep apnea: Interrupted breathing while asleep may lead to stroke.
Schedule an Appointment At Vejthani Hospital
With the costs of preventative carotid artery treatment being extremely affordable, no person should subject themselves to the dangers of incurring a stroke. Seek medical attention if your lifestyle puts you at risk of developing carotid artery disease.
Diagnosis
The doctor will be performing a physical assessment as well as a medical history review, by assessing for signs of bruit, a swooshing sound that can be heard over your neck’s carotid artery showing that the artery is narrowed, as well as assess your speech, memory and strength. Furthermore, these tests may be recommended by the doctor:
- Ultrasound: Checks blood pressure and flow in the carotid arteries.
- Computerized Tomography (CT) or Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Shows any signs of stroke or other unusual signs.
- CT angiography or Magnetic Resonance (MR) angiography: Shows a more clear view of the carotid arteries in your neck and your brain by injecting a contrast dye to the blood vessel.
Treatment
Treatment of carotid artery disease aims to avoid the occurrence of a stroke. Furthermore, treatment is based on how much plaque is accumulated in the carotid arteries.
Mild to moderate obstruction may be treated by:
- Changing your lifestyle: Lose weight, stop smoking, reduce salt intake, eat healthy and do regular exercise to decrease atherosclerosis development.
- Medication: Medication to manage high blood pressure and decrease cholesterol level. Aspirin or other blood-thinners to avoid blood clots may be prescribed by the doctor.
For severely clogged arteries or those that have experienced TIA or stroke, the doctor may suggest to remove the blockage. The following procedures may be performed:
- Carotid endarterectomy. This is usually the first choice of treatment for carotid artery disease. An incision will be made on your neck to open the damaged blocked artery and take out the plaques. The artery will then be stitched or repaired by grafting.
- Carotid angioplasty and stenting. A local anesthesia will be used and a catheter with a tiny balloon will be inserted to the blocked artery. The balloon will then be inflated to expand the artery and a stent (a small wire mesh coil) will be placed to keep the artery wide. This procedure is done if the clog is not accessible by carotid endarterectomy or if you have other underlying disease that makes the surgery complicated to be performed.