Acute lymphocytic leukemia
Overview
Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) is also called acute lymphoblastic leukemia. ALL is a type of cancer that is found in the blood and the bone marrow. In acute lymphocytic leukemia the disease affects the white blood cells called lymphocytes. It progresses rapidly and forms immature blood cells that invade and eventually outnumber the mature ones. This type of leukemia is the most common type of cancer in children and has a very high chance of being cured. It can also occur in adults, but even with treatment the chance of a cure is greatly reduced.
Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of acute lymphocytic leukemia may include:
- Bleeding, such as frequent nosebleeds and bleeding from the gums
- Bone or joint pain
- Fever
- Frequent infections
- Swollen lymph nodes in and around the neck, armpits, abdomen or groin
- Pale skin
- Shortness of breath
- Weakness and fatigue
Causes
When there is a change in the DNA (genetic material) of the bone marrow, leukemia occurs. The DNA is what tells the cell what to do and instructs it when to grow as well as when to die. But in acute lymphocytic leukemia this doesn’t happen, and therefore the mutations cause the bone marrow to continue growing and dividing.
As this happens, there is a problem with blood cell production, and the bone marrow will produce immature cells and those will in turn develop into leukemic blood cells (lymphoblasts). Then all of these abnormal cells that have been generated are unable to properly function and they also crowd out the healthy cells.
Risk factors
There are some factors that may increase the risk of acute lymphocytic leukemia, which include:
- Previous treatment with specific types of chemotherapy
- People exposed to very high levels of radiation
- Patients with genetic disorders, especially those with Down’s Syndrome, have a higher chance of obtaining ALL.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia
A patient exhibiting symptoms of acute lymphocytic leukemia will be physically checked for swollen glands, and a blood sample will be taken. If the sample proves to have an abnormally high level of white blood cells, it could be a sign of acute leukemia and the patient will be referred to a hematologist. The hematologist will take a small sample of the patient’s bone marrow to examine under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis.
As this form of leukemia is an aggressive disease that can progress quickly, treatment generally begins within a few days of diagnosis and is usually done in three stages.
The first stage is remission induction, which aims to kill the leukemia cells in the bone marrow and restore the balance of red and white blood cells. Resolving the patient’s symptoms is also part of the first stage.
The second stage is consolidation. This stage focuses on killing any remaining leukemia cells in the body. After that is the maintenance stage. This stage consists of regular chemotherapy treatments to prevent the leukemia from returning. While chemotherapy is the main treatment for acute lymphocytic leukemia, the patient may also require antibiotics, blood transfusions or a stem cell transplant to achieve a cure.
The doctors in the Life Cancer Center at Vejthani Hospital will answer any questions you may have about leukemia so you’re aware of your options.
Diagnosis
There are many ways as the following to diagnose acute lymphocytic leukemia:
- Blood tests. Blood tests are used to determine the amount of white blood cells, in order to see if there is an excess or an insufficiency as well as to determine if there are enough red blood cells and platelets. In the blood test we may also see the presence of immature cells (blast cells) which are usually found in the bone marrow.
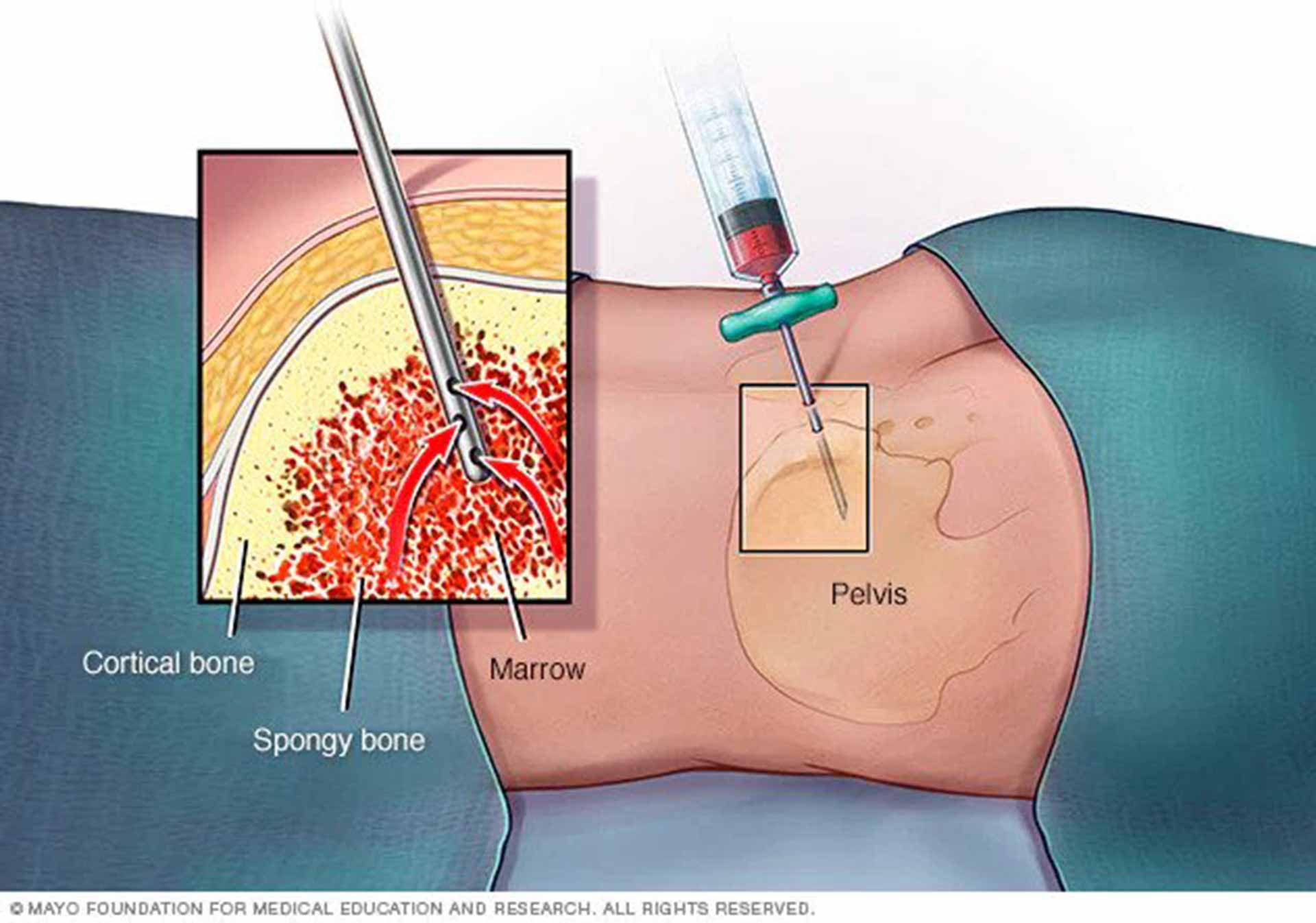
- Bone marrow test. In this test a sample is obtained through bone marrow aspiration and biopsy where a needle is used to take a sample of the bone marrow and then this sample will be further tested for leukemia cells. These cells will then be divided in to specific types based on their shape, size and genetic components, as well as certain changes in the cancer cells and determine whether the leukemia cells began from B lymphocytes or T lymphocytes.
- Imaging tests. In order to see whether the cancer has spread to the brain and spinal cord or any other organs, an X-ray, a Computerized Tomography (CT) Scan, or an ultrasound will be used.
- Spinal fluid test. The spinal fluid that is around the brain and spinal cord may be used as a sample in order to monitor if there is a spread of cancer cells to the spinal fluid.
In order to determine on which level the condition is, the following factors will be looked at:
- The type of lymphocytes whether they are B cells or T cells
- The genetic changes which are in your leukemia cells
- Your age
- Results from lab tests
Treatment
There are various phases in the treatment for acute lymphocytic leukemia. These phases can reach up to two to three years:
- Induction therapy. The first phase of treatment will be used in order to destroy most of the leukemia cells in the blood and bone marrow and this will then in turn help to restore normal blood cell production.
- Consolidation therapy. This is the post-remission therapy and in this phase the most important part is to focus on the destruction of any leukemia cells that may remain in the body.
- Maintenance therapy. This is the third stage and used for prevention of the cells from regrowth. In this stage the treatment is given at lower doses and therefore takes a long period of time.
- Preventive treatment to the spinal cord.
Patient with acute lymphocytic leukemia may receive additional treatment to kill leukemia cells located in the central nervous system during each phase of therapy. Chemotherapy drugs are often injected directly into the fluid that covers the spinal cord.
Treatments are as follows:
- Chemotherapy. This way is used as an induction therapy for both adults and children. It is drugs that are used to kill the cancer cells and can be used in consolidation and maintenance phases.
- Targeted therapy. This kind of therapy is treatment with drugs which focuses on specific abnormalities that are found in cancer cells. If these abnormalities are blocked then it will cause the cancer cells to die. However, the cancer cells need to be tested prior in order to see if targeted therapy will help to destroy them. This kind of treatment can be used alone or with other combinations of
- Radiation therapy. This kind of therapy uses high-powered beams to kill cancer cells. It can be used also when the cancer has spread to the central nervous system.
- Bone marrow transplant. Also known as stem cell transplant, is used in order to treat relapse if it occurs. It helps in order to increase the healthy bone marrow by replacing the leukemic bone marrow from a person that is leukemia free. Prior to the bone marrow transplant, there must be high doses of chemotherapy or radiation in order to destroy the bone marrow that is producing leukemia cells firstly.
- Engineering immune cells to fight leukemia. This treatment uses chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cells which are germ-fighting T cells and creates them to fight cancer cells and then after that returns them back into the body. This treatment can be used for treating consolidation therapy or relapse in children and young adults.




