Knee pain that occurs from Osteoarthritis is a prevalent issue among older adults. As we age, the knee joints that have supported our body weight for years can deteriorate due to the breakdown of articular cartilage. This cartilage acts as a cushion between the joints and facilitates smooth movement. Its deterioration causes a loss of flexibility and increased friction when moving. This gradual wear down of the smooth tissue protecting the knee joint causes knee pain, resulting in Osteoarthritis.
Indicating Signs of Knee Osteoarthritis
- Knee pain during movement, especially when standing up or kneeling
- Inability to sit up or climb up the stairs
- Popping or grinding noises in the knee when moving
- Swollen and inflamed knee joint
- Deformed knee joint
- Stiff knee joint, difficulty bending or fully straightening the knee compared to its usual range of motion
What Happens During a Knee OA Diagnosis?
The doctorwill first examine your knee joints for signs of pain, swelling, and movement capabilities. Imaging tests may be required for further investigations. It could be X-rays or MRI to examine the bones and soft tissues like cartilage if a clearer image is needed.While blood tests can’t diagnose Osteoarthritis directly, they can help rule out other conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis. In some cases, doctors may perform a joint fluid analysis. This involves drawing fluid from the affected joint with a needle and analyzing it to identify the cause of pain. This can help differentiate between Osteoarthritis and other issues like gout or infection.
Treatment options for Osteoarthritis
The goal of treatment is to reduce pain, improve the functions of your knee, and slow the progression of Osteoarthritis.
- Medications: Manages pain and inflammation
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Limiting Knee Flexion: Avoid activities that require bending your knee over 90 degrees.
- Strengthening Exercises: Focus on the quadriceps muscles can help support your knee joint
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy body weight reduces pressure on your knee joints
- Therapy:
- Physical Therapy: Personalized physiotherapy programs can strengthen your joint muscles, improve flexibility, and ultimately reduce pain. Low-impact exercise like swimming or walking can be equally effective.
- Occupational Therapy: Helps you to perform everyday tasks without straining your affected joints.
- Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS): This approach applies low-voltage electrical currents to manage pain, particularly for knee osteoarthritis patients.
- Surgery and other Procedures:
- PRP Therapy: Platelet-rich plasma Therapy has emerged as a promising treatment method for managing knee osteoarthritis. PRP injection uses the patient’s own concentrated platelets, rich in growth factors, to stimulate healing and reduce inflammation in the knee joint. After the patient has withdrawn blood, it will be placed in a centrifuge, a special machine that spins the blood at high speed. This spinning process separates the blood components, concentrating the platelets in the plasma. The concentrated PRP is then carefully extracted from the centrifuged blood and injected directly into the affected area of your knee joint. PRP can be given to patients with all stages of knee OA.
- Lubrication Injection: A substance containing hyaluronic acid, similar to the natural fluid in healthy joints, can help relieve pain by providing a cushioning effect in the knees.
- Stem Cell Therapy: Stem cells have a unique ability to develop into different types of cells, including those that make up cartilage and help cushion the joints. There are many sources of stem cells for OA treatment, including the patient’s own stem cells to help repair damaged tissues in the joint or stem cells from umbilical cord blood or the patient’s bone marrow, fat tissue, or cartilage. These cells are then processed and injected directly into the knee joint. Once in the joint, the stem cells can help reduce inflammation, promote tissue regeneration, and potentially slow down the progression of knee OA. While stem cell therapy shows promising results in treating OA, more research needs to be done to fully understand its effectiveness and long-term benefits. It’s essential to keep in mind that it is still a choice for treatment for knee OA knee and not a standard treatment method.
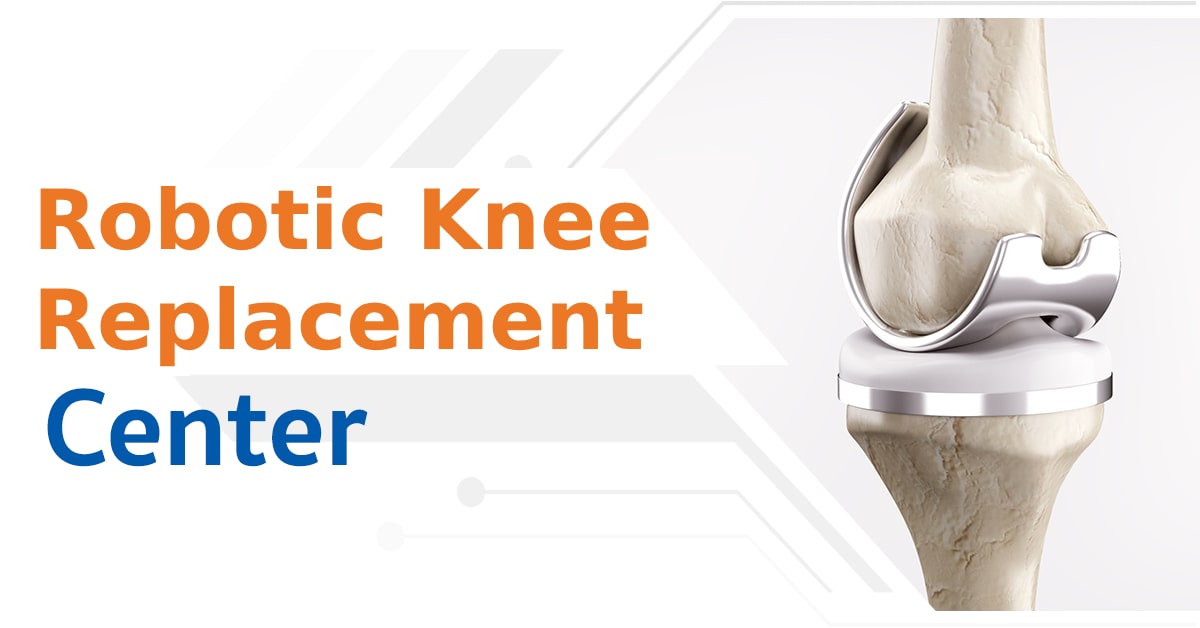
- Total knee Arthroplasty: A solution for severely damaged knee joints. The surgeon replaces the worn-out joint surfaces with artificial implants made of medical-grade plastic and titanium- or cobalt-chromium-based alloys. Advancements like robotic-assisted knee replacement surgery or Rosa Knee surgical robots have enhanced the precision and effectiveness of TKA, potentially reducing the risk of complications and errors.
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, seeing a specialist for proper diagnosis and treatment is crucial. Treatment options depend on the severity and cause of knee pain. The primary approach is oral medications or injections. Some individuals with severe Osteoarthritis may require knee replacement surgery. Advancements in medical technologies like robotic knee replacement surgery have shown promising improvements in recovery and enabled patients to regain their previous lifestyle, allowing them to stand and walk again in 12 hours after the surgery.
For more information, please contact
Robotic Knee Replacement Center 1st Floor, King of Bones Building, Vejthani Hospital
Call: (+66)2-734-0000 Ext. 2222
English Hotline: (+66)85-223-8888
- Readers Rating
- Rated 4.9 stars
4.9 / 5 ( Reviewers) - Spectacular
- Your Rating