The signs and symptoms of breast cancer may start when cells in the breast begin to grow out of control. The cancer spreads very rapidly into and around the breast tissue and will typically travel either through the lymphatic system, or through blood vessels to other parts of the body.
30% of breast cancer cases are hereditary and an abnormal gene also play a role in developing breast cancer. Consuming a high-fat diet is associated with increased risk of breast cancer.
According to a new study published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, these women are at an increased risk of developing breast cancer:
- Women who take the Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) for a long period of time.
- Women who are overweight have a 1.5-2.0 times higher risk of breast cancer than women who are not overweight.
- Women who hit early menopause before 45, have been linked with breast cancer, while late menopause has 2 times a lower risk.
- Women who don’t have children have a 30-70% higher risk of breast cancer than women who have children. Having the first child after age 30 also increases the risk of breast cancer. The younger you are when you have your first child, the lower your risk.
- Women with extremely dense breast tissue are more likely to develop breast cancer. The genetic make up affects breast density.
Adult women of all ages are encouraged to perform breast self-exams at least once a month. The best time to do breast self-examination is 7-10 days after the last menstrual cycle when your breasts are less swollen and tender. If you are no longer menstruating (such as after menopause), breast self-examination should be performed on the same day each month. Women under age 50 who no longer have a uterus, try to do the exam on day when your breasts are not swollen.
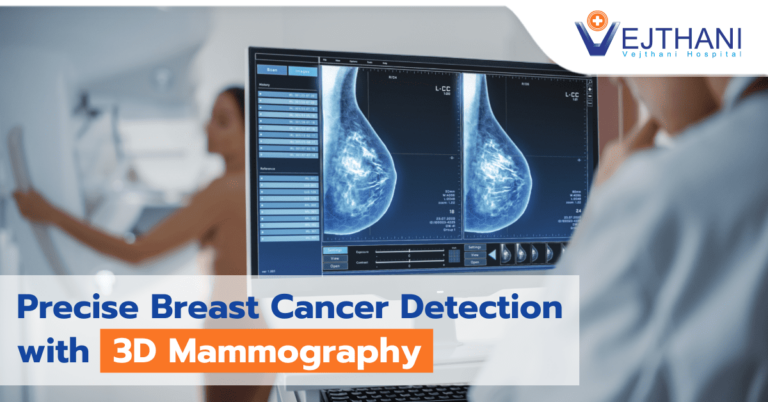
Mammography
Mammography is a specialized medical imaging that uses a low-dose x-ray machine to detect early breast cancer signs and symptoms. They can also be used to detect and diagnose breast disease in women experiencing symptoms such as a lump, pain, skin dimpling or nipple discharge. If something suspicious is found on a mammogram, the radiologist will read the mammogram to look for abnormalities. The images may be 4 times enlarged to make it easier to see the suspicious areas. An additional ultrasound examination may be required to diagnose the abnormality.
Unlike analog mammography, digital mammography is a mammography system in which the X-ray film is replaced by electronics that convert X-rays into mammographic pictures of the breast. The images captured by digital mammography are transferred to a computer for review by the radiologist and for long term storage using a PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System). These systems handling digital mammograms can store and expand images provided in compression formats meeting DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) standards for storing and transmitting medical images.
Advantages of Digital Mammography
- Digital mammograms can be displayed on electronic displays.
- Digital mammography captures high resolution medical images well suited for the detection of the signs of early breast carcinoma.
- Digital mammography uses about 30-60% less radiation than Analog.
- Patients spend less time in the exam room as there is no waiting for X-ray film to be developed.
- Brightness, darkness, or contrast can be adjusted and sections of an image can be magnified after the digital mammogram is complete.
- Patients rarely need to return for repeat images due to under or over exposures.
- Digital mammography provides incredibly sharp and clear images of breast tissue.
- Digital mammograms are safe and relatively painless, and they often take more views of each breast than the analog type.
- The images are immediately available for the radiologist to review.
Detecting the signs of breast cancer early increases the treatment options and survival rates. Though when to begin mammography and at what interval to repeat it is a personal decision, an annual mammogram is generally recommended for women above 40 years old.
Breast Ultrasound
Breast Ultrasound is an imaging test that sends high-frequency sound waves through your breast and converts them into images on a viewing screen. Besides detecting symptoms of breast cancer, this examination is used to assess breast tissue, it’s also used to assess blood flow to areas inside the breasts, and often used along with mammography.
Ultrasound Elastography
Ultrasound elastography is an emerging set of imaging modalities used to image tissue elasticity and are often referred to as virtual palpation. These techniques have proven effective in detecting and assessing many different pathologies, because tissue mechanical changes often correlate with tissue pathological changes.
Signs of breast cancer start when cells in the breast begin to grow out of control. The cancer spreads very rapidly into and around the breast tissue and will typically travel either through the lymphatic system or through blood vessels to other parts of the body.
Vejthani Hospital offers comprehensive treatment and care for women with breast cancer at our Life Cancer Center. Take control of your health by making an appointment for a breast examination at Vejthani Hospital today.
For more information, please contact
Breast Center, Vejthani Hospital.
Call: (+66)2-734-0000 Ext. 2715
English Hotline: (+66)85-223-8888
- Readers Rating
- Rated 4.8 stars
4.8 / 5 ( Reviewers) - Spectacular
- Your Rating