Health Articles
Mouth Cancer: Early Signs, Risk Factors, Prevention and Treatment
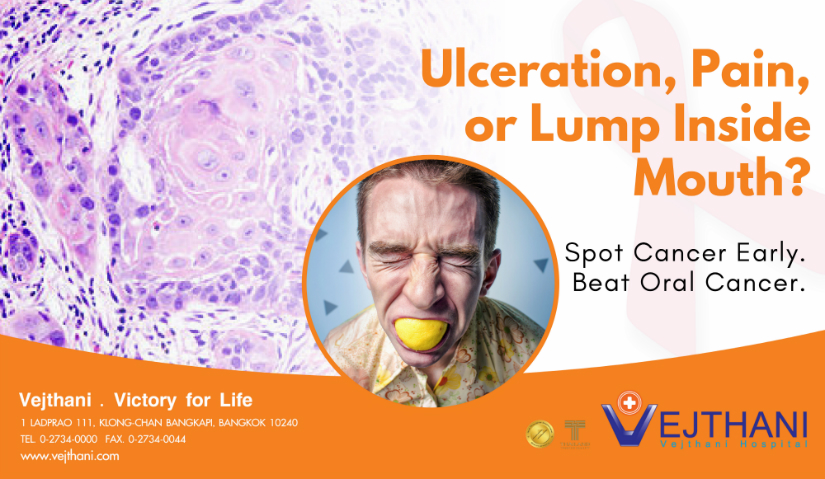

Have you ever noticed something wrong going on inside your mouth? Maybe it’s time for you to see your dentist. A simple ulceration, pain, or lump might be something else or could already be cancerous.
Mouth cancer refers to cancer that develops in any of the parts that make up the mouth. Mouth cancer can occur on the:
- Lips
- Gums
- Tongue
- Inside lining of the cheeks
- Roof of the mouth
- Floor of the mouth
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Oral Cancer?
- Swellings/thickenings, lumps or bumps, rough spots/crusts/or eroded areas on the lips, gums, or other areas inside the mouth
- The development of velvety white, red, or speckled (white and red) patches in the mouth
- Unexplained bleeding in the mouth
- Unexplained numbness, loss of feeling, or pain/tenderness in any area of the face, mouth, or neck
- Persistent sores on the face, neck, or mouth that bleed easily and do not heal within 2 weeks
- A soreness or feeling that something is caught in the back of the throat
- Difficulty chewing or swallowing, speaking, or moving the jaw or tongue
- Hoarseness, chronic sore throat, or change in voice
- Ear pain
- A change in the way your teeth or dentures fit together
- Dramatic weight loss
Who Are Susceptible to Oral Cancer?
- Smokers. Cigarette, cigar, or pipe smokers are six times more likely than nonsmokers to develop oral cancers.
- Smokeless tobacco users. Users of dip, snuff, or chewing tobacco products are 50 times more likely to develop cancers of the cheek, gums, and lining of the lips.
- Excessive consumption of alcohol. Oral cancers are about six times more common in drinkers than in nondrinkers.
- Family history of cancer.
- Excessive sun exposure, especially at a young age.
- Human papillomavirus (HPV). Certain HPV strains are etiologic risk factors for Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OSCC)
How Is Oral Cancer Diagnosed?
As a part of your routine dental exam, your dentist will conduct an oral cancer screening exam. More specifically, your dentist will feel for any lumps or irregular tissue changes in your neck, head, face, and oral cavity. When examining your mouth, your dentist will look for any sores or discolored tissue as well as check for any signs and symptoms mentioned above.
Your dentist may perform an oral brush biopsy if he or she sees tissue in your mouth that looks suspicious. This test is painless and involves taking a small sample of the tissue and analyzing it for abnormal cells. Alternatively, if the tissue looks more suspicious, your dentist may recommend a scalpel biopsy. This procedure usually requires local anesthesia and may be performed by your dentist or a specialist. These tests are necessary to detect oral cancer early, before it has had a chance to progress and spread.
How Is Oral Cancer Treated?
Oral cancer is treated the same way many other cancers are treated — with surgery to remove the cancerous growth, followed by radiation therapy and/or chemotherapy (drug treatments) to destroy any remaining cancer cells.
What to Do To Prevent Oral Cancer?
- Don’t smoke or use any tobacco products and drink alcohol in moderation (and refrain from binge drinking).
- Eat a well balanced diet.
- Limit your exposure to the sun. Repeated exposure increases the risk of cancer on the lip, especially the lower lip. When in the sun, use UV-A/B-blocking sun protective lotions on your skin, as well as your lips.
- Conduct a self exam at least once a month. Using a bright light and a mirror, look and feel your lips and front of your gums. Tilt your head back and look at and feel the roof of your mouth. Pull your checks out to view the inside of your mouth, the lining of your cheeks, and the back gums. Pull out your tongue and look at all surfaces; examine the floor of your mouth. Look at the back of your throat. Feel for lumps orenlarged lymph nodes in both sides of your neck and under your lower jaw. Call your dentist’s office immediately if you notice any changes in the appearance of your mouth or any of the signs and symptoms mentioned above.
- See your dentist on a regular schedule. Even though you may be conducting frequent self exams, sometimes dangerous spots or sores in the mouth can be very tiny and difficult to see on your own. The American Cancer Society recommends oral cancer screening exams every 3 years for persons over age 20 and annually for those over age 40. During your next dental appointment, ask your dentist to perform an oral exam. Early detection can improve the chance of successful treatment.
Vejthani Hospital Dentalis Center
Dentalis in Vejthani Hospital pride ourselves as one of Thailand’s dental clinics with comprehensive dental services ranging from regular check-ups, personal diagnosis and customized treatment plan, cosmetic and implant dentistry, and many more. With our excellent field in dental health, oral cancer can be taken care of and can be diagnosed early as much as possible upon regular visits.
Because we truly care for our patients’ satisfaction and dental health, our clinic is constantly improving our treatment and service standard. Our certified team of dedicated dentists together with the latest hi-technology dental instruments and modern facilities is our guarantee to you that our dental service is definitely excellent. Furthermore, the environment is relaxing and above all highly hygienic. Thus, rest assured that you will get the satisfactory results.
Service Hours
Day Time
Monday to Saturday 09.00 am – 08.00 pm
Sunday 09.00 am – 05.00 pm
Appointments & Inquires
Phone : +66 (0) 2734-0000 ext. 3000, 3004
Fax : +66 (0) 2734-0375
Location
Vejthani Hospital, Dentalis Center, 2nd floor.